IT Risk

The more your company relies on technology, the more crucial it is for organizations to understand IT Risk, and also how to effectively identify and manage it.
Threats can stem from equipment failure to targeted cyber attacks. Here we present explanations for what is an IT Risk and the different types of technology risks that could affect your business.
Also included, is a simple computer risk management checklist to help you handle any potential IT threats or risks that your business may face.
On this page:
Defining IT Risk
IT Risk is the threat poised to business data, critical systems and different business processes when an IT vulnerability is exploited. The exploitation of an IT vulnerability could lead to disruption, breach, or failure, ultimately causing harm to the organization.
Unmanaged technology risk, or information technology (IT) risk, has the potential to significantly disrupt a business. Poorly managed, or uncontrolled IT risks can severely damage a business, often resulting in:
- Financial & monetary losses
- Loss of privacy
- Reputational damage
- Legal or compliance implications
- Potentially loss of life

Companies can face many types of technology risks from several sources, such as information security breaches, cyberattacks, insider data theft, service outages, and more.
Every type of technology risk has the potential to cause financial, reputational, regulatory, or strategic harm to the business. Consequently, businesses must have an effective technology risk management strategy in place to anticipate and address any potential problems.
Categorizing Technology Threats
Threats to your technology assets can stem from several sources, impacting multiple elements of an organization.
Businesses need to be aware of the different types of threats, as well as the potential impact areas. For simplification, threats to your technology assets can be categorized based on areas of impact as follows:
- Security – Compromised business data due to unauthorized access or usage
- Availability – Inability to access the computer system that is needed to carry out business operations due to system downtime
- Performance – Poor productivity due to slow access to computer systems
- Compliance – Breach of legislation due to the failure to adhere to legal binding or mandatory regulations or standards
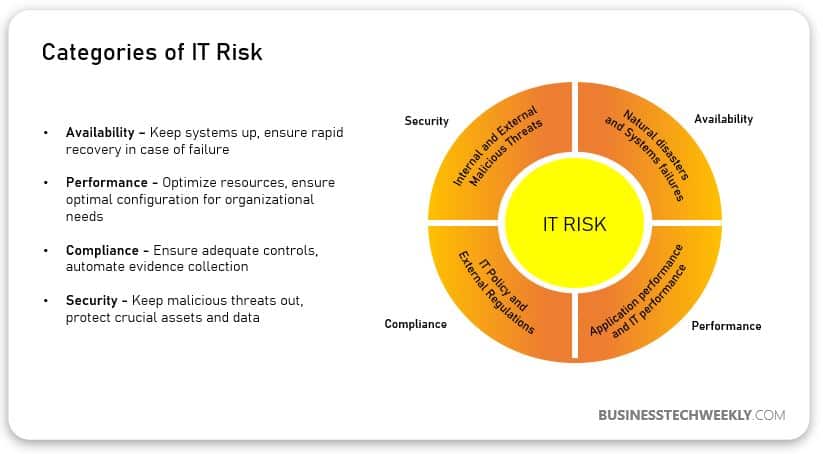
The impact of Technology Risk
For businesses reliant on technology, failure to mitigate against IT threats could result in:
- Data theft or damage
- Financial theft or loss
- Reputational or brand damage
- Damage to the company’s assets
Where technology failure affects the laws and regulations, poorly managed or uncontrolled IT Risks can also lead to:
- Breach of lawful duties
- Violation of the privacy of the client’s information
- Penalties, fines and litigation
- Damage to the companies’ reputation
Most businesses rely on sophisticated technology to connect and transact with suppliers, customers and other stakeholders. The data collected from these communications and transactions may be subject to data privacy. Such data may be vulnerable if organizations neglect to manage or control technology threats effectively.
To prevent exposing your business to potential disruption, potential threats need to be evaluated and measured. You can find out more about how to carry out a proper computer risk assessment and learn more about the computer risk management process.
Types of Technology Risk
Threats to IT systems or technology can either be external or internal and can be intentional or accidental. Once an a threat is realized, i.e. the threat is active and affecting your business, you may find that your business is unable to:
- Achieve its business goals
- Continue service
- Maintain business reputation and customers
- Avoid further breaches or threats
Focussed on growing and driving your business, technology threats can often be overlooked. Regardless of the size or nature of your business, or the industry you operate in, your technology systems and data can be vulnerable to technology risk.
Examples of Information Technology Risks
- Physical threats – Resulting from access or damage caused to the technology resources like internet servers. Physical threats can include theft, fire or flood, or unauthorized access to private data by another worker or outsider.
- Electronic threats – Compromising your business data. For example, a cyberattack may result in ransomware being installed. See Types of Malware to learn more.
- Technical failures – Hardware or software failure could lead to corrupt or lost data.
- Infrastructure failures – Loss of service, such as business internet connection, which may impact productivity and disrupt the business operations.
- Human error – This is a significant threat; someone might delete important information, or fail to adhere to security procedures properly.
Businesses and organizations, look to technology to make them unique from competitors, leverage the cost benefits, such as those offered by SaaS cloud applications, and keep their overheads low.
It is, therefore, imperative that businesses have a robust IT Risk management strategy in place.
While an IT Risk assessment can help prevent and avoid business disruption, you should also look at Business Continuity Planning, to limit the effect of any disruption.
Managing Technology Threats
IT Risk Management is the process of correctly identifying, controlling and keeping proper information security or technology risks to lessen their negative impact.
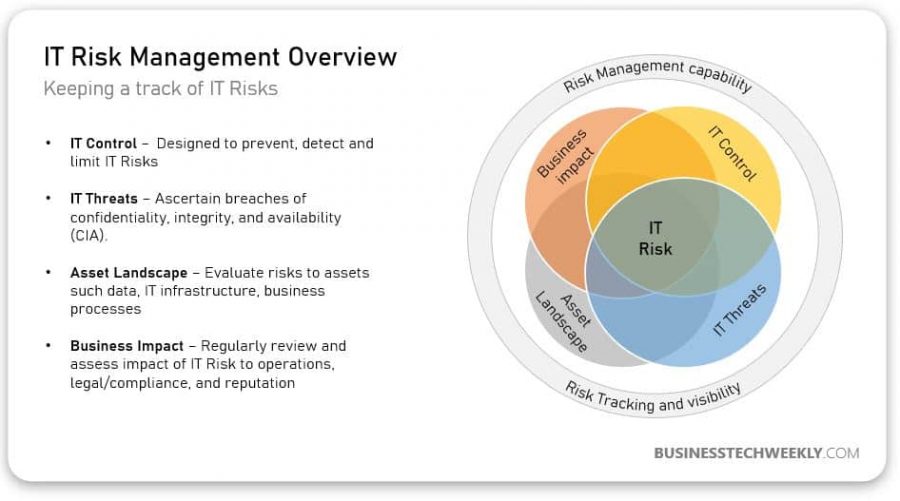
How To Manage Technology Risk
Managing different types of computer risks starts with identifying what they are:
- Different types of threats that affect the business
- What assets could be impacted by cyber threats?
- Methods of making the computer systems secure
Find out more about the methods on how to carry out a computer risk assessment and learn more about the computer risk management process.
The National Security Centre offers risk management guidance for dealing with cybersecurity threats.
IT Risk Management Process
To effectively manage threats to your technology assets, follow the below steps for implementing a robust risk management strategy:
- Identify risks – Make sure to determine the dangers of nature and how they can affect your business.
- Assess risks – Determine the seriousness of the threat and how it affects the business and adequately prioritize these risks. Carry out a technology threat assessment.
- Develop a fast response to the incident – Develop comprehensive plans for managing the issue and recover from the IT.
- Document and report – Document your plans and ensure that key stakeholders and resources are kept informed.
- Implement and control – Put in place the preventive measures to reduce the risk from occurring and limit the risk’s impact on the business.
- Review specific procedures and processes – Continue to assess certain threats and handle new risks.

IT Risk Management Checklist
Risk management is simple to deal with if you follow certain principles. To handle these technology risks to run the business properly, make sure that you take these following steps:
- Look for computer risks that can affect the whole business. Identify the probability, costs and the aftermath. Carry out a complete technology risk assessment.
- Think about the choices, capability or what could cause potential attacks. Try to understand the motives of potential cyberattacks.
- Assess the severity of computer risks and address, as a priority, the most crucial ones.
- Understand any regulations and legislations, such as meeting GDPR requirements, or adherence to PCI DSS.
- Do not just rely on one technical sign-in method. Use two-factor authentication to make sure the user identity adequately confirmed.
- Produce robust data recovery and data backup procedures. You can leverage the cloud to conduct backups.
- Support technical control of the whole policies, procedures and training. Understand the most common threats in Cybersecurity.
- Ensure that your business has a robust business continuity plan. Regularly review and update the plan. Read more about computer risks and business continuity.
- Establish effective crisis management. Ensure that there are incidents that you can test and improve incident planning and recovery.
- Set up computers, servers, firewalls and other systems securely. Update software and hardware equipment. Read more about cloud computing security issues and challenges, and securing your wireless network.
- Develop and document computer policies and procedure, such as internet and online usage, making sure that the staff knows what falls under acceptable use.
- Consider qualification to the computer security management standards for the business and the trading partners.

