Why is Cybersecurity Important for Small Businesses?

Cybersecurity has always remained one of the biggest challenges. It will not be any different in this speed-driven world of digitization. Rapid technological advancement resulting from growing needs for global connectivity has brought about a rise in cybercrime in the past few years.
While it is easy to think that data breaches only happen with large companies, small to mid-sized businesses are being equally impacted. Several challenges must be tackled to make cybersecurity a core aspect of any business strategy.
Small companies are, in fact, one of the most common targets for attackers. Below, we explain why cybersecurity should be an essential consideration for small business owners.
On this page:
Why Hackers Target Small Businesses?
Regardless of its size and industry, every business has weaknesses that hackers can exploit for personal gains. Just because a business is small or does not possess critical data assets does not mean it is unattractive to cybercriminals.
There are several reasons why small firms and start-ups are, at times, more likely to be targeted than enterprises:
Customer Information
Cybercriminals know that small businesses generally store and handle customer data that is easy to offload for a profit.
These companies often gather sensitive information about customers, including their social security numbers, bank account credentials, medical records, transaction history, and other personal details.
Third-Party Vulnerabilities
Hackers target SMBs as they are often associated with larger companies and third-party suppliers and can easily give them entry points into those valuable networks.
As more prominent companies are sometimes harder to penetrate, attackers target small businesses that partner with them to get into the more effective systems.
The Target breach of 2013, for example, resulted in a theft of 40 million credit and debit cards occurred because of vulnerabilities in a third-party vendor.
Lack of Resources and Support
While more influential organizations generally have dedicated teams for cybersecurity, many small businesses assign these duties to people handling other daily operations at the company.
As a matter of fact, up to one-third of SMBs admit there is no function in the company dedicated to IT security.
Multiple Interfaces
Another common reason for increased attacks for small businesses is the increasing number of IoT devices creating interfaces for network attacks.
These organizations turn to IoT devices to leverage their benefits for growth and reduced costs. Hackers exploit weak devices to get into more critical networks.
Lack of Finances
As start-ups often work on tight budgets, they cannot prioritize cybersecurity. They avoid spending on resources, training, and consultants for information security and ignore the latest updates and patches, leaving their systems vulnerable to attacks.
Inadequate Training
Small businesses are so busy establishing themselves that they neglect to train, educate and monitor employees.
As a result, this often increases the risk of cyberattacks. Cybercriminals know how to penetrate through the weakest links. These employees often download potentially malicious content from the internet or fail to secure their login credentials.
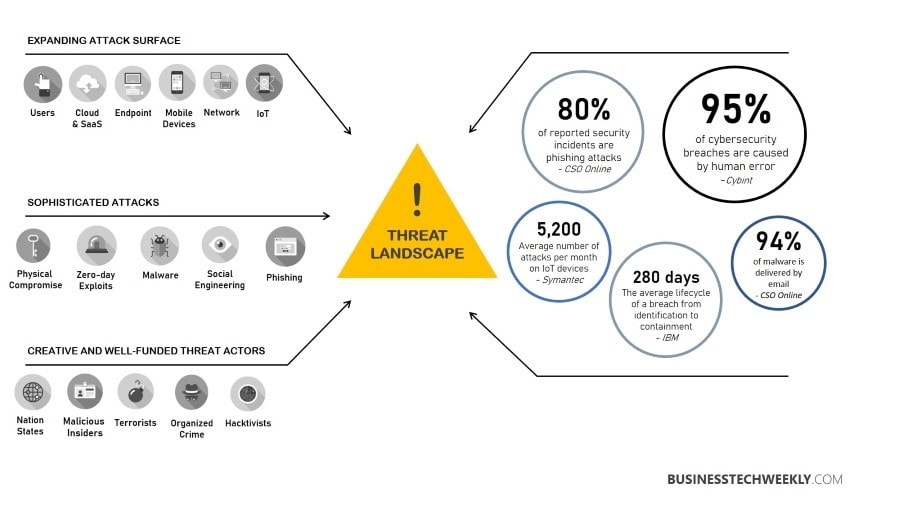
How to Evaluate Cyber Risk
Before taking steps to improve cybersecurity posture, a small business owner should have a clear picture of the business’s risks.
Understanding the risks is essential when implementing processes and strategies associated with cybersecurity. It helps make informed decisions to justify expenditures related to security measures.
Without a proper understanding of risks, all the decisions and efforts are like hitting a shot in the dark.
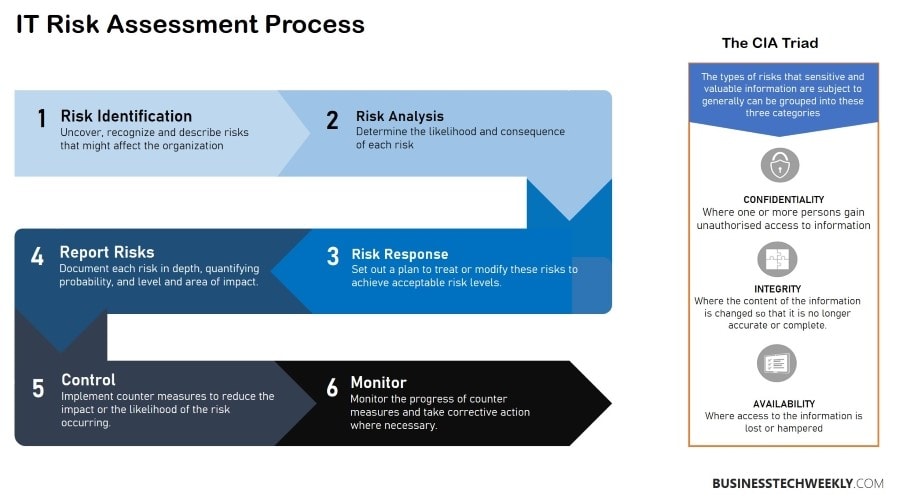
There are several definitions of risk, but a general equation is
Risk = Threat x Vulnerability x Impact
The product of these three factors helps the business owner make informed decisions rather than fear or emotion-based choices. Though it looks like a mathematical formula, it is a logical product.
For example, consider a business owner looking to assess risks associated with the threat of ransomware from hackers on a critical data-containing system.
If the system is critical, which means the loss from the threat negatively impacts the business operations, and the network is vulnerable because of the absence of antivirus and firewall, the risk is probably high.
However, if the company has good defenses in place, vulnerability is low, and hence the risk is moderate even when the system is critical.
Also read: How to evaluate Cyber Risk
Types of Threats for Small Businesses
Small businesses often have a misconception that the business is too small to be a target, but this is not true. Start-ups and SMBs are just as vulnerable as large enterprises.
With digitalization, hackers automate attacks, making it possible to target hundreds and thousands of small companies at once.
Malware Attacks
Malware refers to any software that might cause harm to computers and networks. Viruses and trojans come from downloads, spam emails, and other devices over the network.
Such attacks are quite dangerous for small businesses as they can leave devices crippled, demanding expensive repairs.
Such threats also give hackers a way to access critical data, putting employees and customers at risk. The rise of personal devices in the office environment also increases the risk of malware attacks.
Phishing
The most widespread threats faced by small businesses are email or phishing attacks. These attacks occur when attackers appear trustworthy and entice the user to download malicious content, visit a malicious link, or provide access to critical data, credentials, or account details.
Social engineering has recently emerged as the most dangerous form of a phishing attack.

Ransomware
One of the most prominent types of cybersecurity attacks is ransomware. Ransomware affects many businesses every year.
This type of attack involves forcing the business to pay money to access the attacker has locked data. Small businesses are particularly at risk from such threats due to endpoint protection.
Weak Passwords
Easy to guess, weak passwords can pose a significant threat to small businesses. Most companies use cloud-based services with multiple accounts. When there is no strict password policy, sensitive data and personal information stored in these accounts are compromised.
Small businesses face threats from employees ignoring the importance of strong passwords and frequent changes.
Insider Threats
Another major threat for small businesses comes from the organization’s inside, from business associates, former employees, and current staff. These people can harm critical data from greed, malice, or simply ignorance and negligence.
For SMBs, insider threats are growing as more employees access multiple accounts containing critical data.

Cybersecurity for Small Businesses – Best Practices
Any business, small or big, should have a well-designed cybersecurity policy in place based on the best practices to secure data and applications against existing and emerging threats.
Create a Data Security Plan
The first requirement is to identify who needs access to what data and devise policies to protect the access.
No employee should be given more access than what is required. If people bring their devices to work, ensure a firm protection policy for these devices. You can implement security methods like face recognition, fingerprints, and multi-factor authentication.
Review the security plan regularly and make necessary changes as the business evolves.
Conduct Employee Training
The company should consider educating employees about common threats like malware, spam, ransomware, and phishing.
You should start training the staff as soon as you employ cybersecurity practices. Make sure employees follow these policies and prioritize security all the time. They should only be given access to information when they need it.
Related: Ten tips to improve Cyber Security Awareness amongst your employees
When people leave the company, their accounts should be deleted, and their IDs, badges, and keys should be confiscated.
Such a policy will prevent any threat from former employees trying to take revenge.
Implement Strong Password Policies
Businesses should enforce strict password policies to ensure employees set unique, hard-to-guess passwords and change them often.
For added security, two-factor authentication should also be implemented, preventing any unauthorized access to data and applications.
Also read: 15 Tips for improving password security
Backup Data Frequently
Timely data backups can help you stay protected against ransomware attacks that sabotage your business.
Some businesses prefer uploading encrypted data to the cloud. In contrast, others store backups on physical devices like hard drives and flash drives.
It is good practice to use multiple methods to backup data and do this frequently to reduce the risks of losing critical business information.
Install Firewalls
Firewalls are a great way to prevent malware attacks. Installing a firewall on the network prevents people from visiting suspicious websites and downloading malicious files.
Businesses should focus on having firewall protection on every device, including personal smartphones. Moreover, the firewall should be kept updated to avoid any risks of spam and phishing emails.
Invest in Cyber Insurance
As technology advances, cyberattacks are getting more complex and dangerous. A cybersecurity breach can result in a significant loss for the business, sometimes making it difficult to survive.
Having cyber insurance is one of the best ways to stay protected against the devastating crisis from cyberattacks.
Next Steps
Small businesses face a host of cybersecurity challenges and generally find it harder to recover from incidents if they occur.
The best way for a small business to protect itself from these threats is to have a solid cybersecurity program in place. It is easy to protect employee and customer data with the correct precautionary measures, thereby building trust and loyalty while avoiding losses from any security compromise.
By investing some resources, you can save yourself a great deal of time, money, and effort in the long run.

