Data Privacy vs Data Security: Which Should You Prioritize?

Data Privacy vs Data Security: It can be challenging to differentiate data security privacy from data security. Before deciding whether to invest in data privacy or security, business managers must be able to distinguish between the two.
Examine these principles and the policies, processes, and technologies that support them to ensure that the data your customers and employees entrust to your organization is handled appropriately and secured throughout its lifecycle. This will help prevent malicious or unintentional misuse or loss of data.
This post will briefly discuss both their similarities and differences. We shall also demonstrate that neither can exist without the other.
On this page:
Data Privacy vs Data Security
Commonly, organizations feel that if they protect sensitive data from hackers, they are immediately compliant with data privacy rules. This may not always be the case.
Data Security and data privacy are typically used synonymously, although there are fundamental distinctions between the two:
- Data Security safeguards information from both external and internal threats
- Data Privacy governs the collection, sharing, and utilization of data
Consider a situation where you have taken considerable measures to protect personally-identifying information (PII). The data is encrypted, access is restricted, and various monitoring systems overlap.
However, if this PII was gathered without the appropriate consent, you may violate a data privacy rule, even if the data is secure.
What is Data Privacy?
Typically, companies utilize data privacy — a guideline for data processing and gathering that takes the sensitivity of the data into account — to regulate who has access to personally identifiable information and personal health information.
Birthdays, names, social security numbers, financial, contact and medical information, are common types of information under data privacy guidelines.
The most prevalent data privacy concerns are:
- Managing contracts or policies
- Using a controlling regulation or law (like General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR)
- Third-party management
In general, privacy refers to an individual’s right to be free from interference and prying eyes or the right to be left alone.
It’s critical for businesses because you’ll almost certainly get sensitive, personal information from your shareholders, customers, and employees. Because an organization is responsible for protecting the private information of multiple parties, businesses must guarantee that data is only accessible to authorized individuals.
Furthermore, data is critical to your organization’s ability to grow, review finances, and perform other tasks. Data privacy helps establish who can lawfully view and use such information because it must be accessible to critical staff members.
Data privacy is critical for many organizations since only authorized parties can access sensitive information and data.
By implementing stronger data privacy safeguards, your firm can prevent thieves from accessing and utilizing data for nefarious purposes. As you know who has access to your data, you’ll be able to detect issues when they arise.
Aside from protecting enterprises from criminals, data privacy is critical to your organization’s regulatory compliance. When a business fails to comply with data privacy rules and guidelines, it may face fines and a loss of public trust.
Your organization may safeguard its reputation and avoid hefty penalties by adhering to data privacy guidelines.
What is Data Security?
Data security prevents unauthorized access, corruption, and theft throughout digital information’s lifecycle. It encompasses all aspects of information security, from physical hardware security to administrative and access controls of software applications.
In addition, it includes policies and procedures for the organization.
Robust data security measures, when effectively implemented, protect an organization’s information assets not just from cybercriminal activity but also from insider threats and human error, which are still the leading causes of data breaches today.
Implementing tools and technology that raise an organization’s awareness of where its vital data is stored and how it is utilized is required for data security.
Ideally, these systems should be able to implement measures such as encryption, data masking, sensitive file redaction, and automated reporting to accelerate audits and assure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Encryption – Encryption keys scramble data by using an algorithm to convert normal text characters into an unreadable format only authorized users can read. Encryption solutions protect sensitive file and database volumes by disguising their contents using encryption or tokenization.
The majority of systems also incorporate security key management features.
- Data Erasure – Data erasure is more secure than normal data wiping. Data erasure uses software to overwrite data on storage devices and confirms that the data cannot be recovered.
- Data Masking – Businesses can allow teams to develop applications or train individuals using real data by masking it. It conceals personally identifiable information (PII) as appropriate so that development can occur in compliant contexts
- Data Resiliency – An organization’s ability to withstand or recover from any failure that affects data availability – determines its resilience. Recovery time is crucial for minimizing impact.
What are the differences between Data Security and Data Privacy
In conclusion, data privacy and data security are not synonymous. Data privacy involves gathering, utilizing, storing, and deleting data. Data security comprises policies, strategies, and mechanisms for protecting sensitive data.
Consequently, if you use a Google Gmail account, your password would be an example of data security, while how Google uses your information to operate your account would be an example of data privacy.
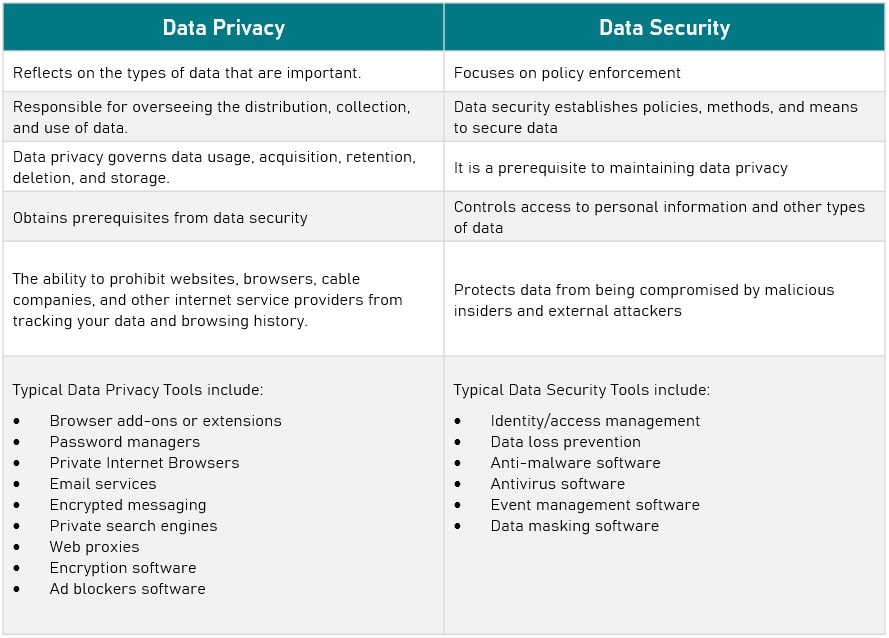
However, the former cannot exist without the latter. Data privacy is contingent upon data security. And information security is an essential precondition for data privacy.
Tips for implementing data privacy and data security
Since data privacy and protection go hand in hand, you would likely want to implement them correctly in your organization. Below are some essential guidelines for adopting successful data privacy and protection regulations.
1. Professional expertise is a must
Before establishing data privacy and data protection policies and methods, your firm needs to collaborate with professionals in the industry. Because appropriate data privacy can help organizations avoid legal and credibility issues, many organizations employ professionals to adopt data privacy standards.
For instance, your firm may engage policy, engineering, and legal specialists to design or evaluate data privacy solutions.
Countries worldwide realize that tight guidelines aimed to protect personal data privacy are in the best interests of both organizations and individuals. The European Union’s General Data Protection Law (GDPR) is the most stringent regulation to date, with other countries basing their regulations on the GDPR’s privacy obligations.
Some notable examples include the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Brazil’s Lei Geral de Protecao de Dados (LGPD), and Canada’s proposed Digital Charter Implementation Act.
Similarly, you can engage IT specialists and other data security experts to develop data privacy solutions for your firm. Since data protection is required to safeguard vital information and your organization’s activities, it is advantageous to employ these professionals to provide proper security methods.
By consulting with data privacy and data protection specialists, your firm can protect data in the most secure manner possible.
RELATED: 10 Cybersecurity Frameworks designed to help businesses reduce risks
2. Limit employee access to sensitive data
Human error is a leading reason for data breaches and non-compliance with legislation. Due to human mistakes, it is frequently advisable to restrict employee access to sensitive information and data.
The fewer staff members that have access to sensitive data, the less likelihood of errors or incorrect use of information.
You will still need to give employees access to the information they need to perform their tasks. As you select the level of access you wish to grant your employees, you should evaluate who needs certain types of data and how you intend to monitor data usage.
You may limit the likelihood of human mistakes by restricting data access to only those who require it and by educating your personnel to handle it correctly.
The three pillars of information security:
- Confidentiality – Safeguarding critical information from reaching the wrong people while allowing the right people to use it
- Integrity – Ensuring information’s consistency, correctness, and trustworthiness throughout its existence; and
- Availability – Ensuring that the data is accessible when needed
These are referred to as the C-I-A triad and must be addressed to attain a desirable level of information security.
3. Automate as much as possible
In addition to limiting data access to avoid errors, you can automate a significant portion of your data security and privacy operations to reduce the likelihood of human error. Your security and compliance responsibilities can be easily automated with a data privacy and protection solution.
For instance, automating your data categorization operations can free up personnel for other tasks and reduce classification errors.
Since it might be difficult for staff members to recall every regulation and compliance law they must follow while doing everyday tasks, automating data compliance can make their work easier.
As a result, your staff won’t have to worry as frequently about fulfilling compliance standards and won’t be placed in situations where they’re prone to make mistakes.
Similarly, automated protection solutions can limit the likelihood of data breaches and assure the completion of numerous operations without error.
Data Privacy vs Data Security: Striking the right balance
When comparing Data Privacy vs Data Security, one thing is clear, organizations should not favor one over another.
However, digital marketers wishing to increase their cybersecurity expertise should understand the relationship between data security and data privacy.
Though there are several reasons why front-end developers should focus more on enhancing data security and updating systems to ensure data privacy.
The primary consideration here is how your company can construct an optimal security system to strengthen ROI and client loyalty.

