Threat Detection and Response: Best Practices

Threat detection and response is the topmost priority for cybersecurity teams. However, with so many newly emerging threats, an effective threat detection and response system can often seem daunting. The key is to break down threat detection and response to their most basic elements.
Here, we present the basics of threat detection and delve into the best practices to identify and handle threats.
On this page:
What is Threat Detection?
The term ‘threat detection’ relates to cybersecurity and refers to anything that can cause potential harm to a network or computer system. Threats and attacks don’t mean the same thing.
Threats show the potential for attacks, while attacks represent the act of harming or intruding on a system or network.
RELATED: Threat Management Challenges
Threat detection is the process of identifying threats on computer systems, networks, or software in an attempt to detect them before they can turn into attacks. This task often involves extensive data processing in an organization, particularly in large environments, and is automated.
Most organizations consider automation a necessity for advanced threat detection and monitoring.
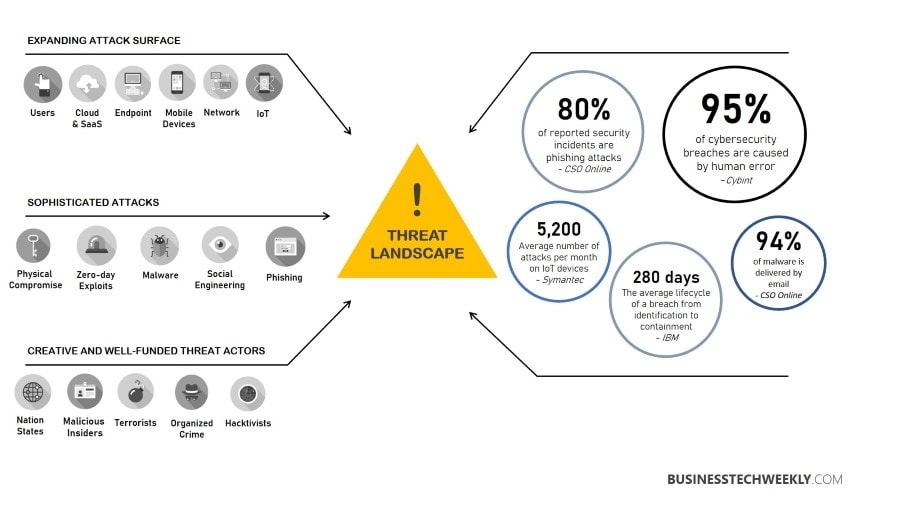
What do the Cyber Attackers want?
A threat detection process should prioritize focusing on the most valuable resources to the organization and what information is the most vulnerable to attack.
Attackers are generally opportunistic and target outdated devices as entry points. This is more common after significant updates that publicize vulnerabilities.
In most cases, the attackers’ end goal is often monetary. However, here are the five most common things cybercriminals are after.
Personally Identifiable Information
PII (Personally Identifiable Information) is specific to individuals. PII includes information used for identity theft, such as bank account details and social security numbers. Criminals may either use your information to spend on your behalf or impersonate you.
User Credentials
Stealing user credentials is often an easy way for attackers to access a network. They don’t need the personal information of users but rather network login credentials to get entry into sensitive resources. Increased scamming and weak passwords can make this easier.
Some attackers would use the privilege escalation technique to give themselves additional privileges they can use to get what they are after.
Intellectual Property
Attackers can be nation-states who are after stealing trade secrets to benefit their economies. Sometimes, competitors are looking to fill gaps in their strategies and gain an advantage at the cost of their rivals.
Employees may steal critical secrets or pass over rival information for promotion. Companies should protect their trade secrets and intellectual property against attackers hired by competitors in the market.
RELATED: 10 Steps to prevent insider data misuse and theft
Revenge
Some ex-employee attackers seek revenge and are after slowing down the company’s systems. Sometimes, opponents may even deface web pages to embarrass government agencies or organizations.
Ransom
As it goes unexplained, attackers are primarily motivated by monetary gains. They target individuals and companies for money by using ransomware to encrypt and lock server or endpoint files and demand a ransom to unlock them.
DDoS attacks are also common where servers and networks experience bogus traffic load until the ransom is paid.
Types of Threats
Organizations, small or big, face threats of several types. Threat detection involves identifying different threats to help security teams craft strategies for risk mitigation. Some of the common types of threats are:
Malware
Malware is any threat that infects the computer or network in the form of spyware, viruses, ransomware, or trojan horses.
RELATED: Types of malware businesses must protect against
Such malicious software can cause several issues like theft of sensitive information, disabled or interrupted services, breakdown of network framework, or unauthorized control over applications.
Phishing
Phishing refers to the act of tricking users into disclosing personal information. Electronic communication methods like emails and website forms are common phishing techniques.
Users generally reveal personal information or credentials to criminals who send fake messages disguised as genuine communication.
Ransoms
Criminals may hold resources or information until a ransom is paid to them. A popular method is to encrypt the organization’s data and hold its encryption key.
Some attackers may even use DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks to make the resources unavailable until they are paid a ransom.
RELATED: Responding to a Ransomware Attack: Initial steps businesses must take
DDOS
This type of attack generally floods servers and networks with unnecessary traffic to put a load on the resources and website. The attackers infect systems with malware to control them remotely.
Devices are then converted into zombies or bots and instructed to send requests to a specific network to cause a considerable spike resulting in a traffic overload.

How to Detect Threats?
Looking at the significance of threat detection, cybersecurity packages come loaded with built-in threat detection technologies and features, some of which are:
- Endpoint detection and response
- Threat intelligence platforms
- Cloud access and security brokers
- Security information and event management systems
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems
- User and entity behavior analytics
- Network firewalls and honeypots
The primary advantage these solutions offer is their ability to identify and respond to threats in real-time automatically.
By monitoring the data activity across endpoints and detecting behaviors, these tools can catch potential attacks that could otherwise go undetected.
Best Practices for Detecting and Responding to Threats
Here are some of the best practices organizations should follow when implementing threat detection and response solutions:
- Select tools and techniques that offer real-time threat protection. Even in the presence of the best preventative solutions, continuous monitoring in real-time is crucial for security teams.
- Log all the endpoints serving as network access points.
- Boost the efficiency of threat detection tools with measures including encryption, data classification, and restricted controls.
- Security teams may not be able to monitor all the activities occurring during the day. To cope with this limitation, use tools that send alerts for risky activities, thus allowing the IT people to do their work until a problem arises.
- Consider the human factor and educate employees to minimize threats in the organization.
- Have an incident response plan prepared to address an inevitable attack that gets through anyway despite preventative measures.
RELATED: 10 tips to improve Cyber Security Awareness amongst your employees
In Summary
Threat detection and response are essential to maintaining security in an organization, but it is only the starting point. Threat response is crucial to handling identified threats, so most detection tools offer response features.
These solutions automatically identify and block threats and execute patches to protect the systems. Some others may provide the security teams with the ability and guidance to deal with high-risk threats.

