What is Security Governance? Core Components and Best Practices

Security governance keeps your data safe.
It’s the rules that protect you from cyber threats. Consider it a playbook for your company’s digital safety team.
Guidelines and reports shape these practices, helping you stay one step ahead of hackers.
Agencies like NIST offer support, providing tools and advice to ensure that your strategies are effective.
As threats increase, so does the need for robust governance. It’s a matter of building trust and keeping information safe.
On this page:
What Is Security Governance
Security governance is a formalized approach to overseeing your organization’s cybersecurity risk and compliance.
It’s about ensuring that security objectives are aligned with business and financial goals, while ensuring compliance requirements are met.
The approach would inform how resources—including appropriated funding for technology, personnel, and training—should be targeted.
It requires the establishment of executive roles focused on compliance and information security.
Definition and Key Concepts
Governance is another key part of cybersecurity governance, with frameworks such as NIST or ISO providing guidance on how to mitigate cybersecurity threats.
Effective information security governance is a key component to protecting your organization’s digital assets, establishing the standard for policies that direct organizations.
These policies advance a whole-of-government approach to threat management, making security measures proactive and responsive to the most pressing needs.
Objectives of Security Governance
The overarching goals are to better align security efforts with the organization’s goals and objectives by introducing a transparent management structure, without compromising sensitive information.
This helps organizations stay ahead of industry standards and requirements.
It helps improve the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
Components of Security Governance
Key components of security governance include, but are not limited to, risk management, compliance, and incident response.
A clear and robust governance structure breeds security by design through ongoing vigilance and evolution.
Advanced tools such as vulnerability scanners greatly improve the organization’s ability to both prevent and respond to cybersecurity incidents.
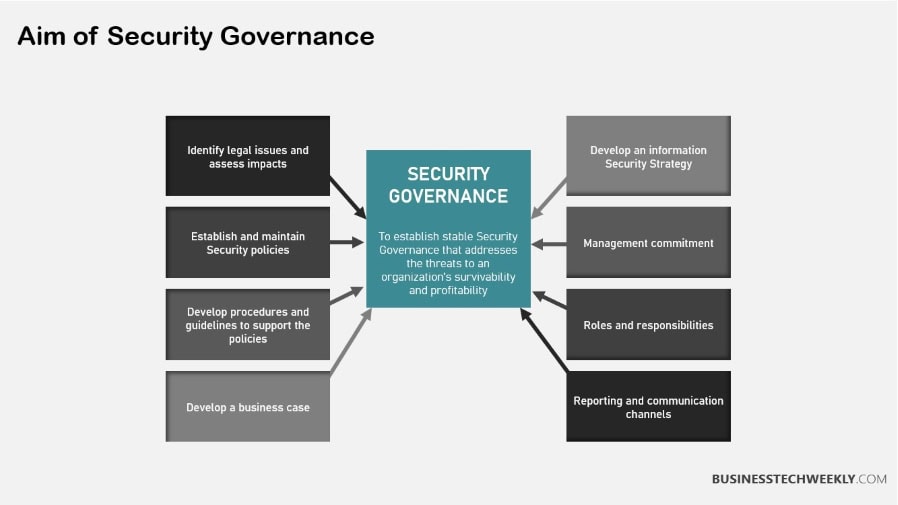
Importance of Security Governance
This is where security governance comes in and why it’s so important to further protect your organization.
Enhancing Risk Management
Implementing proactive risk management strategies is key to identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities.
Supporting Compliance Requirements
Strong governance frameworks ensure that your organization is complying with applicable laws and regulations, including HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA.
Protecting Organizational Assets
Prioritizing the protection of sensitive data means implementing strong security governance.
Core Components
Security Governance refers to the overall framework that ensures security policies, procedures, and controls are effectively designed, implemented, and managed to protect an organization’s information and assets.
The core components of Security Governance ensure that an organization’s security measures are aligned with business objectives, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices, while providing robust protection against evolving security threats.
The core components of security governance include:
Security Policies
Clear and comprehensive policies define the organization’s security objectives, acceptable use, data protection, and compliance requirements.
Risk Management
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating security risks is central to governance.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Adherence to industry standards, laws, and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS is crucial.
Governance Frameworks
Security frameworks provide a structured approach to implementing security controls.
Leadership and Oversight
Effective security governance requires strong leadership, including a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or equivalent, along with a governance body or committee (e.g., Security Steering Committee) to ensure ongoing oversight and decision-making related to security.
Roles and Responsibilities
Clear definitions of security roles, responsibilities, and accountabilities within the organization are vital.
Incident Response and Reporting
A defined process for handling security incidents, including identification, containment, recovery, and communication.
Security Awareness and Training
Ongoing training programs and awareness campaigns are necessary to ensure that employees are informed about security risks and know how to follow security protocols to reduce human errors and insider threats.
Monitoring and Auditing
Regular audits and continuous monitoring of security systems, controls, and policies ensure that the governance framework is effective and that any breaches or vulnerabilities are detected early.
Performance Metrics and Reporting
Metrics such as incident response times, audit findings, risk assessments, and compliance levels help measure the effectiveness of security governance.
Continuous Improvement
Security governance is not static; it requires regular updates to adapt to evolving threats, technological changes, and business needs.
Roles and Responsibilities
Leadership and Management
The role of executive leadership in driving security governance initiatives is akin to setting the sail’s direction.
It starts with key stakeholders, including the CEO, CFO, general counsel, head of compliance, and board members. They all play a vital role in shaping the organization’s security culture.
Whenever leadership shows a strong commitment, it trickles down through the organization; you influence the culture of security.
This isn’t some boxes to be checked — it’s an approach where infosec is an integral part of what we do day to day.”
Management commitment is key; it sets the tone for how seriously security is taken. When the top brass is all in, it sends a message to everyone else.
Members must know what is expected of them, and leaders must be clear about that.
This means sharing priorities and goals so everyone knows what’s up and where they fit in.
A Data Owner is a steward of information, while CISOs and IT managers focus on frameworks that support the CIA principles: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Employee Involvement
Leadership alone can’t do it all; employees need to be in the loop too. The first step to encouraging active participation in security governance is awareness and training.
Once people know why and how to be secure, they’re more willing to contribute.
Think about it as creating a security-minded culture with everyone from interns to senior staff taking some responsibility.
The first thing to nurturing this culture is making security everyone’s responsibility. It’s not just about top-down directives.
Listening to employee feedback can seriously boost security policies and practices.
Employees are in the field, identifying real-world problems and recommending actual solutions. This type of engagement enhances the overall security posture of the organization.
External Partners
I want to briefly touch upon external partners. They’re almost like extensions of the team in the governance process with security.
Collaboration with partners can bolster security measures significantly.
It’s really important to have clear expectations and agreements with third-party vendors.
This means checking in with them regularly and assessing that their security practices meet yours. Imagine it like this: if you’re working with a vendor, you want to know they’re as invested in protecting your data as you are.
Regular assessments help keep everyone accountable and ensure governance policies align with the organization’s security framework.
By taking this approach, you’re looking out for your own interests while ensuring that your partners follow through on their obligations.
Best Practices for Effective Security Governance
Align with Industry Standards
In aligning your security governance with industry standards, start by identifying key frameworks like ISO/IEC 27001 or NIST that inform best practices.
Staying compliant with these frameworks not only boosts your credibility but guarantees that you’re meeting necessary security standards.
Regularly updating your practices is crucial because standards are constantly changing.
A well-designed GRC model provides a useful framework to briefly sketch key roles and compliance responsibilities.
That’s why it’s important to talk in a language that resonates with C-suite leaders so you can align security efforts to support broader business objectives.
Use Technology Solutions
Without a doubt, technology is a key component in strengthening security governance.
Deploy tools that improve visibility and speed with real-time monitoring and advanced threat detection, helping to reduce response times by up to 90 percent.
By eliminating manual processes, automation makes security operations more efficient and effective.
Codifying security policies streamlines management, and solutions like Privileged Access Management ensure only authorized access.
AWS services like Workload Discovery can assist in keeping up to date inventories of resources and their relationships between them, continually honing your governance model.
Engage Stakeholders
By engaging stakeholders at every level, you can create a culture of security cooperation.
Engaging with IT, legal, and compliance teams during the governance strategy development process will help ensure all bases are covered.
Articulating the importance of governance in a way that is understandable to all parties fosters organization-wide buy-in.
Ongoing security training and incorporating security expectations into job descriptions help create a more security-savvy workforce that’s better equipped to keep compliance.
Monitor and Adjust Continuously
Setting up clear metrics to measure the effectiveness of security governance is critical.
Frequent reviews and strategy changes, informed by monitoring results, ensure you’re one step ahead of threats.
Being flexible in your governance approach will help you stay responsive in the face of emerging challenges.
Make sure your security strategy aligns with your organization’s needs and risk tolerance with their resources.
Implementing Security Governance Frameworks
1. Establish Clear Policies
Building a strong foundation starts with knowing what security policies you have in place.
2. Define Roles and Responsibilities
Assigning specific roles further enhances accountability and clarity with the organization’s structure.
3. Integrate with Business Strategy
Aligning security governance to business strategy means any security measures are in place to support operational efficiency and innovation.
4. Conduct Regular Audits
Regular audits are critical for evaluating the value and impact of security governance efforts.
5. Foster a Security Culture
Creating an environment that recognizes the importance of security awareness is key.
Challenges in Security Governance
Security governance is a critical foundation for protecting your organization’s information assets.
Key Points to Remember
- Security governance offers a systematic methodology in handling cybersecurity risks. It provides for the ongoing maintenance of that compliance with clear and consistent policies, processes and practices.
- Good security governance works toward achieving your organizational mission. It increases accountability and secures sensitive information by setting specific goals and adopting industry best practices.
- Risk management, compliance, and incident response make up the core of security governance. To be successful, they all require long-term oversight and evolution.
- To better protect your organization, be proactive in how you manage risk and meet regulatory requirements. Secure your digital assets by putting strong security controls in place.
- Establishing a security governance framework involves formulating clear policies, assigning roles, integrating with business strategy, conducting regular audits, and fostering a security culture.
- Overcoming such challenges demands a proactive stance against evolving threats, with a focus on balancing security and usability and optimizing resource constraints.
Understanding Security Governance: FAQs
What is Security Governance?
Security governance is the framework you use for overseeing and controlling how an organization approaches security.
It aligns security initiatives with business objectives, where they belong, so risks are appropriately managed.
Why is Security Governance Important?
It helps make sure that security enables business objectives. Getting everything aligned helps protect assets, keep things compliant, and reduce risk.
That’s a key to building trust with stakeholders.
What are the Core Components of Security Governance?
The core components are policies, procedures, roles, responsibilities, and metrics.
These elements provide a framework for how to handle security risks.
Who is Responsible for Security Governance?
In practice, top management, including the board of directors, is typically responsible.
They connect security to the strategic business goals of the organization.
How Can Organizations Implement Effective Security Governance?
Organizations can implement it by defining clear policies, assigning roles, and regularly reviewing security practices.
Continuous training and awareness programs are also crucial.
What Are Some Effective Practices in Security Governance?
Some effective practices include conducting regular risk assessments, updating policies, and engaging with stakeholders.
Continuous improvement and adapting to new threats are also key.
How Does Security Governance Benefit an Organization?
It improves decision making, mitigates risks, and boosts compliance.
It secures the organization’s reputation and assets.

