ISO 27001 Implementation Checklist

Many organizations are embarking on an ISO 27001 implementation to implement information security best practices and protect their operations from cyber-attacks. Many businesses will be aware that ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard designed to support the adoption of a robust Information Security Management System (ISMS). This ISMS covers people, processes and technology, and addresses specific security threats faced by organizations. Here, we detail the steps you can follow for ISO 27001 implementation. In addition to the checklist, provided below are best practices and tips for delivering an ISO 27001 implementation in your organization.
On this page:
Implementing ISO 27001
Compliance with the ISO 27001 standard is globally recognized as a hallmark of best practice Information Security Management. Certification demonstrates to customers, stakeholders and staff alike that an organization is serious about its data security responsibilities. Related: What is ISO 27001?

When implementing the ISO/IEC 27001 standard, many organizations realize that there is no easy way to do it. Many businesses find implementing ISMS challenging because the ISO 27001 framework needs to be tailored to each organization. Consequently, you will find many specialist ISO 27001 consulting firms offering different implementation methods. These varying approaches allow the delivery of an Information Security Management System (ISMS) unique to your organization. However, when setting out to achieve ISO 27001 compliance, there are typically five crucial stages your initiative should cover. We cover these 5 stages in more detail in the next section.
ISO 27001 Checklist: 10 Steps to Implementation
To help you in your efforts, we’ve created a 10 step checklist, which covers, explains, and expands on the five crucial phases, providing a comprehensive approach to implementing ISO 27001 in your organization.
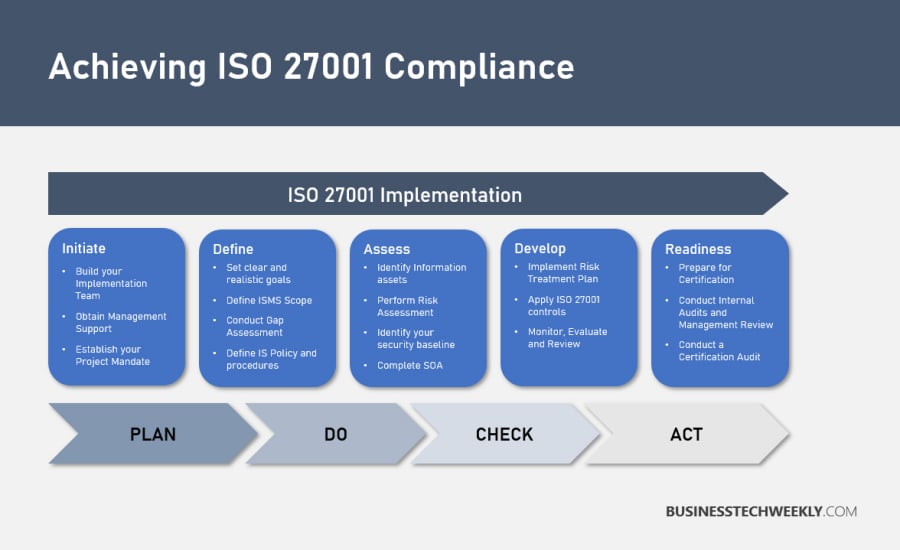
The steps below can be used as a checklist for your own in-house ISO 27001 implementation efforts or serve as a guide when assessing and engaging with external ISO 27001 specialists. Here is the list of 10 steps to help implement ISO 27001:
1. Initiate your ISO 27001 ISMS project
The purpose of this first step is to establish a team, with management support and a clear mandate, to implement ISO 27001.
- Appoint a Project Leader – The first task is to identify and assign a suitable project leader to oversee the implementation of ISO 27001.
- Build your Implementation Team – Your team should have the necessary authority to lead and provide direction. Your team may consist of cross-department resources or external advisers.
- Purchase a copy of the ISO27001 standard – It would be a good idea to have the latest version of the standard available for your team to understand what is required for success.
- Identify and contact Certification Bodies (CB) – Identifying suitable external consultancy, known as Certification Bodies, at this stage will give you a ‘feel’ for the market. You will need to hire an accredited CB to perform the certification audit.
- Obtain Management Support – You need to have senior management approval and commitment (from a resource, budget, and concept perspective) for deploying an information security management system and attaining ISO27001 certification.
- Establish your Project Mandate – Your team must have a clear understanding of why ISO 27001 certification is required and what you hope to achieve from it.
2. Identify the strategic and organizational positioning of the ISMS
The objective is to develop an implementation plan. You can achieve this by adding more structure and context to your mandate to provide an overview of your information security objectives, risk register and plan. To do this, consider the following:
- Set clear and realistic goals – Define the organization’s information security goals and objectives. These can be derived from the organization’s mission, strategic plan and IT goals.
- Identify the return on investment – Four costs need to be considered when implementing this type of project, internal resources (including management, HR, IT, facilities and security), external resources (experienced consultants), certification, implementation (dependent mainly on the health of IT within the organization).
- Identify relationships with other management systems and certifications – Organizations have many processes already in place, which may or not be formally documented. These will need to be identified and assessed for any possible overlap, or even replacement, with the ISMS.
- Define your ISO 27001 implementation scope – Define the scale of your ISMS and the level of reach it will have in your daily operations.
3. Prepare the Documentation
The aim is to build a concise documentation framework to help communicate policy and procedural requirements throughout the organization. The ISO27001 standard specifies a mandatory set of information security policies and procedures, which need to be created as part of your ISO 27001 implementation to reflect your organization’s specific needs.
- Information security policy and other supporting (specific) security policies – Identifying and documenting your organization’s stance on information security issues, such as acceptable use and password management.
- Processes and Procedures – To put into practice the policy requirements.
- Instructions and guides – To describe how employees should fulfil policy requirements.
- Records, registers and logs – To track and capture the procedures and instructions.
- Other documents and records – Complete any other ISO27001 mandatory documentation. Also, set out outline policies that establish roles and responsibilities, how to raise awareness of the project through internal and external communication, and rules for continual improvement.
- Determine a risk management approach – Risk management lies at the heart of an ISMS. Therefore, it is crucial to develop a risk assessment methodology to assess, resolve, and control risks in accordance with their importance.
4. Implement Training, Education and Culture initiatives
The purpose is to ensure your employees and staff adopt and implement all new procedures and policies. To achieve this, your staff and workers need to be first briefed about the policies and why they are essential. As a next step, further training can be provided to personnel to ensure they have the necessary skills and capacity to perform and execute according to the policies and procedures.
- General Information Security Training – Ensure all your employees have been trained in general information security best practices and understand the policies and why these policies are
- Training for External Resources – Dependent on your scope, you will need to ensure your contractors, third parties, and other dependencies are also aware of your information security policies to ensure adherence.
- Agree an internal audit schedule and assign appropriate resources – If you plan to conduct internal audits, it would be sensible to identify the resources and ensure they are trained to perform such reviews.
- Security incident training (identification, reporting etc.) – Ensure your staff are aware and understand the procedures. In particular, the steps they need to take to identify, report, and action any security incidents.
5. Conduct Risk Assessment Activities
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard permits businesses to define their risk management processes. Whichever technique you decide for your ISO 27001 implementation, your decisions must be based on the results of a risk assessment.
- Provide risk assessment training for asset, control and risk owners
- Identify all supporting assets – Identify the information assets as soon as possible. Moreover, identify the threats your organization is facing and try to understand stakeholders’ needs.
- Perform risk assessment activities – Conduct risk assessments. If you lack resources, prioritize risk assessments according to the criticality of the information asset.
- Identify your security baseline – The minimum level of activity required to conduct business securely is your security baseline. Your security baseline can be identified from the information gathered in your risk assessment.
- Complete a Statement of Applicability (SOA) – The SoA documents which of the ISO 27001 controls you’ve omitted and selected and why you made those choices.
6. Implement your Risk Treatment Plan
Implementing the risk treatment plan allows you to establish the security controls to protect your information assets. Most risks are quantified on a risk matrix – the higher the score, the more significant the risk. The threshold at which a threat must be treated should be identified. There are four approaches to address risk:
- Risk Acceptance – Risks below the threshold are tolerable and therefore do not require any action.
- Risk Reduction – Risks above the threshold can be treated by applying controls, thereby bringing them to a point below the threshold.
- Risk Avoidance – You may have some risks that cannot be accepted or reduced. Therefore, you may opt to terminate the risk by avoiding it entirely.
- Risk Transfer – You may opt to transfer the risk by taking out an insurance policy or an agreement with an external party.
7. Operate, Monitor, Evaluate, and Review
Your ISO 27001 should now be an everyday routine within your organization. However, you won’t know if your ISO 27001 implementation operates correctly as an ISMS unless you review it. The purpose is to determine if the objectives in your mandate have been achieved. Where required, corrective actions should be taken.
- Internal audits – An internal audit allows for ommissions in your ISO 27001 implementation to be identified and allows the opportunity for you to take preventive or corrective.
- Management reviews – Management review should ensure the policies defined by your ISO 27001 implementation are being followed and if the required results have been achieved.
- External audits – External audits can be conducted by a Certification Body or independent ISO 27001 consultants. An external audit can independently and impartially verify that your ISMS implementation meets the ISO27001 standards.
8. Prepare for Certification
Once you have implemented the requirements for ISO 2700, the next step is to prepare for an external audit to obtain an ISO 27001 certification.
- Be prepared – Verify all of the standard has been met and check that policies, procedures, records, and mandatory documentation are complete.
- Review results – Ensure internal and external audits and management reviews have been completed, and the results are satisfactory.
- Choose an accredited certification body – Accredited certification bodies operate to international standards, ensuring your certification is legitimate.
9. Conduct a Certification Audit
The certification audit can be a time-consuming process. You will be charged for the audit regardless of whether you pass or fail. Therefore, it is crucial you are confident in your ISO 27001 implementation’s ability to certify before proceeding. Certification audits are conducted in two stages.
- Stage 1 Assessment: Documentation – The first audit determines whether your ISMS has been developed according to ISO 27001’s requirements. If satisfied, the auditor will schedule a more detailed Stage 2 assessment.
- Stage 2 Assessment: Implementation – Typically conducted six weeks after the first assessment, the Stage 2 assessment will audit your performance against your compliant ISMS.
10. Maintaining your ISMS
Obtaining your ISO 27001 certification is excellent, but your ISMS needs to be maintained in an ongoing process. To maintain your certification, you need to ensure that you adhere to all the ISMS policies and procedures, continually update the policies and procedures in line with the changing requirements of your organization, and regular internal audits are performed. To help maintain certification and to re-certify, many Certification Bodies (CB) offer the following:
- Surveillance Audit (Year 2) – A mini-audit conducted by the Certification Body to validate ISMS ISMS scope extension possible.
- Triennial Audit (Every 3rd year) – A Re-Certification Audit conducted by an accredited Certification Body.
ISO 27001 Implementation: Best Practices
Our comprehensive ISO/IEC 27001 implementation checklist should have provided you with a good overview of the main steps your organization needs to follow to achieve ISO 27001. However, to make your job easier, here are some best practices which will help ensure your ISO 27001 deployment is geared for success from the start.
Choose a Champion for your ISO 27001 Implementation
ISO 27001 will be dealt with as a project, but it’s essential to define the person’s responsibilities clearly. When you start your project without assigning responsibilities, there is a strong possibility that the implementation will never finish. The best way is to handover this charge to a person in charge of information security in your organization. Different companies have different titles for this job, such as Information Security Officer (ISO), Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Security Manager, etc. Some companies have corporate structures for project management, so in this case, the project manager would lead the implementation project. Moreover, an information security expert will be part of that team.
Get management support
Usually not taken seriously enough, top management involvement is essential for successful implementation. Lack of management can be one of the causes of why ISO 27001 deployment projects are unsuccessful – management is either not providing enough money or not enough people to work on the project. If top management is not interested in setting security rules, don’t waste your time and spend your efforts on other tasks. You have to convince top management. For this, you need to understand the benefits you can gain by a successful implementation. You can refer to the Benefits of ISO 27001 for ideas on presenting a case to management.
Manage the implementation costs
When you share the idea of ISO 27001 with managers, they’re not sure about two things.
- What will be the result after investing too much money?
- What will be the maintenance cost of such a complex system?
The truth is yes; you have to invest a lot in ISO 27001 implementation process. However, a successful ISO 27001 implementation provides significant benefits which justify the investment. A significant concern is how to keep the overhead costs low because it’s not easy to maintain such a complex system. Employees will lose lots of time while dealing with the documentation. Primarily the problem arises due to inappropriate documentation or large quantities of documentation.
Ensure the right level of competence and expertise
ISO 27001 implementation is a complex process, so if you haven’t done this before, you need to know how it’s done. You can get the expertise in three ways:
- Train yourself and your employees – In this case, you have to ensure that you and your employees have all the implementation knowledge. It would help if you did this when you don’t want outsiders’ involvement in your company. Create awareness and start training seminars. Furthermore, please provide them with tutorials to learn about implementation. Moreover, it will significantly reduce the implementation time.
- Use a combination of employees and outside consultants – You can perform all the analysis, write the documentation and interviews by yourself. Meanwhile, an outside consultant will guide you step by step during the whole implementation process. It can help if you want to learn more about the implementation process.
- Outsource the majority or all of the implemention – In this option, you hire an outside expert to do the job for you. This option requires minimal effort and the quickest way of implementing the ISO 27001 standard.

ISO 27001 Implementation Tips: Don’t complicate things
Here are some great tips for the successful implementation of ISO 27001.
Only create those documents that are mandatory
For a company of 10 employees, you need a written description of operating procedures. Now the question is how to know which documents are required? For this, you can start with ISO 27001 clause 4.3.1. It will give you an idea of mandatory documents. You can add other documents required by other interested parties, such as agreements between partners and clients and legislation. This documentation aims to help your company keep things simple and easy and don’t get too ambitious.
Let the right people write the documentation
Ensure that you’re avoiding the unnecessary content in the documents. Consultants mostly put too much content in the documents that can be kept short. Let those employees write the documents who will be using these documents in day-to-day operations. They will not add irrelevant parts, and it will make their lives easier.
Show commitment during the early phase
After selecting the right persons for the right job, run training and awareness programs in parallel. If the plans and controls are implemented without proper implementation, things can go in the wrong direction.
Maintain all the documentation
The outdated procedure can be a time-wasting experience. So, ensure that your documentation is up-to-date. You can maintain this by assigning tasks to relevant persons. For example, each document must be held by an owner to keep it updated. Moreover, perform regular checks to remove irregularities. Finally, to remove the nonconformities, corrective and preventive actions must be in place.
Measure your success
You might not consider it as a cost overhead, but somehow it must be taken into account. For example, if you lack objectives, how can you measure the outcome? Moreover, if you have set goals, regularly check the progress of what you have achieved.
Implementing ISO 27001 in your organization
ISO 27001 certification has become desirable because cyber threats are increasing at a rapid pace. As a result, many clients, contractors, and regulators prefer organizations to be certified to ISO 27001. Planning and setting ISO 27001 projects properly at the start of the ISMS implementation is critical, and it’s essential to have a plan to implement ISMS in an acceptable budget and time.

