Transaction processing systems: An introduction to TPS

Transaction processing systems assist users in individual transactions by using transaction processing modes facilitating data transactions inside a full database system that monitors transactional transaction processes and programs together.
These systems foster control and balance within an organization’s procedure management system for acquiring services and goods. It is tasked with the coordination of transaction processing systems application control of distribution and product inventory and the real time systems for management of payment account transactions, and the information processing system, of payroll and sales.
It is ideal for monitoring transactions during online transactions since it provides a temporary delay in purchasing or selling a product.
On this page:
What is a Transaction Processing System (TPS)?
A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is an information system used to gather, store, modify, and retrieve organizational data transactions. Additionally, transaction processing systems strive for predictable response times to queries.
At the same time, this is less crucial in transaction processing systems than in other, more real time processing systems or processing one-time systems. Rather than enabling users to run any application concurrently, a transaction processing system allows only specified, ordered batch transactions to.
The transaction processing system (TPS) further secures the success network failure of each transaction by storing, transferring, and receiving data via a database.
Additionally, it integrates with the business’s point of sale system, or POS, which processes credit cards, produces receipts, and receives and holds cash.
Thus, an online transaction processing system is the e-commerce and transaction processing system’s counterpart for every other online transaction processing system that programs an online store.
RELATED: Online Payment Options for Small & Medium Businesses
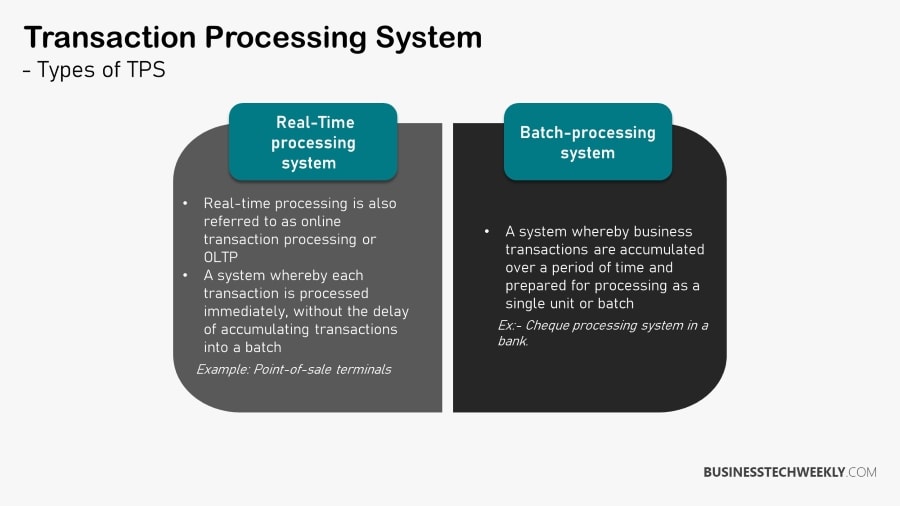
Real-Time vs. Batch Processing
TPS comes in two forms, real-time and batch, transaction processing system modes. In real-time batch transaction processing systems mode, every transaction will be automatically processed as it is made. There won’t be any delays, and as a consequence, the system data will always reveal the transaction’s current status.
For example, in online ticketing, the number of available tickets and seats taken would always be shown in real time processing it. Every change is reflected immediately. In some instances, real-time transaction processing system or real time transaction processing system TPS, will offer more dependable and efficient transaction data.
Every operation will have input data to be saved over time and then processed by a batch processing, or at once for batch processing. For a processing system for instance, an enterprise might decide to process its payroll data bi-weekly. As a result, there will be a postponement or time delay between input data gathering and transaction processing.
Importance of TPS in Modern Business Operations
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) play a pivotal role in the seamless functioning and growth of modern businesses. Their significance stems from their ability to manage and streamline essential transactional activities with precision and efficiency. In a fast-paced business landscape, where time and accuracy are paramount, TPS offer a range of benefits that contribute to enhanced operations and customer experiences.
Efficiency Enhancement
- TPS facilitate real-time processing of transactions, eliminating delays and reducing manual intervention.
- Swift processing ensures smooth customer interactions, contributing to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Automation of routine tasks leads to optimized resource allocation and increased operational efficiency.
Accurate Data Management
- TPS are designed to capture, validate, and store transaction data accurately, minimizing errors.
- Consistent data accuracy ensures reliable reporting, decision-making, and compliance adherence.
- The system’s validation mechanisms prevent incorrect or incomplete data from entering the database.
Informed Decision Making
- TPS provide up-to-date insights into business operations, aiding timely decision-making.
- Real-time data availability enables managers to respond swiftly to market trends and challenges.
- Access to accurate transactional data supports strategic planning and risk management.
Customer Experience Enhancement
- Rapid transaction processing enhances the customer experience, reflecting responsiveness and reliability.
- Seamless online transactions and quick order processing contribute to customer satisfaction.
- TPS-backed customer databases enable personalized interactions and targeted marketing efforts.
Operational Transparency
- TPS offer transparency by maintaining an organized record of all transactions.
- Auditing and tracking capabilities ensure accountability, compliance, and fraud prevention.
- Regulatory and legal requirements are easier to meet due to accurate record-keeping.
Cost and Resource Optimization
- Automation through TPS reduces the need for extensive manual labor, leading to cost savings.
- Streamlined processes minimize wastage of resources, contributing to overall cost efficiency.
- Data-driven insights aid in identifying areas for improvement, promoting resource optimization.
Scalability and Growth Support
- TPS are adaptable to growing transaction volumes and business expansion.
- Scalable architecture ensures consistent performance as the business expands its operations.
- Accommodating increasing demands without compromising efficiency is a hallmark of TPS.
Transaction Processing System Examples
Below are some examples to help you understand the concept:
Real-Time Transaction Processing System Examples
- Reservation systems – Reservation systems are beneficial in any sector where a product or service is reserved for a specific consumer (e.g., layby, train tickets). In such a case, the goods or service is kept until a fair response time.
- Point-of-sale (or POS) terminals – Used by retail enterprises to sell products and services, POS terminals lower the cost of bulk data processing by transforming data to a format easily transmitted over a communication system. For example, the correct product pricing is returned after inputting the product number into a POS terminal.
- The library’s lending system – Used to maintain track of borrowed things, which may be identified by the user’s card and the barcodes on the products. Similar to reservations systems (which maintain product, availability, usage, and maintenance information).
Batch Transaction Processing System Examples
- Cheque Clearance – A written instruction to a bank directing that funds be transferred to a designated account. They are placed into individuals’ bank accounts. It is necessary to establish if the individual has sufficient financial resources (which takes three days). After a check is cleared, money is withdrawn.
- Credit Card Transactions (Manual) – A credit card impression is imprinted on a credit slip, which a sales clerk fills up. The bank receives and processes all impressions in a single batch.
An impression of the credit card is made on a credit slip, which a sales clerk fills up. The bank receives all impressions collectively. Not processed immediately. Customers can view real-time credit card transactions, although the data are updated in batches.
How Transaction Processing Works
TPS is an information system that stores, collects, retrieves, and alters data transactions for an organization. It will also try to offer predictable and rapid response time times for predictable requests, especially for processing transactions in real-time.
Instead of allowing multiple users together to operate arbitrary time-sharing programs, TPS only allows structured and predefined transactions. Most transactions will therefore be of short duration, while the activity for every transaction will be programmed well in advance.
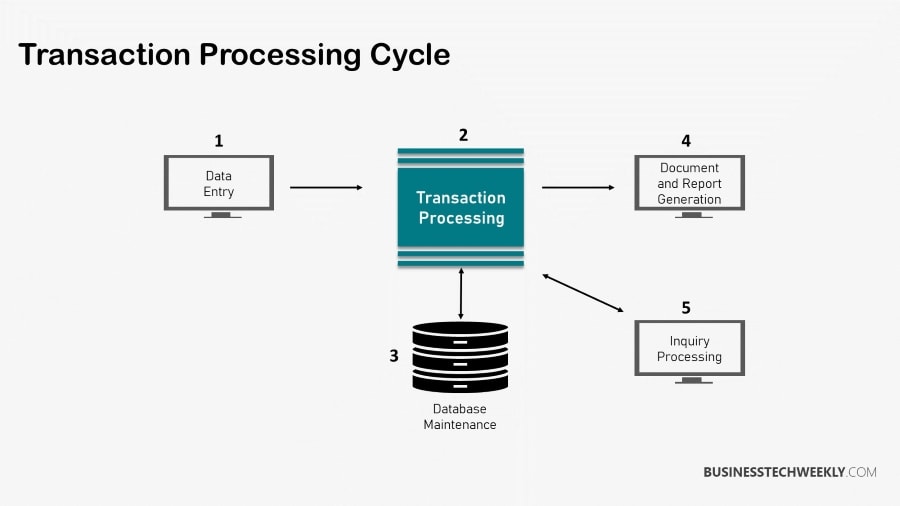
TPS comprises four components: outputs, inputs, storage devices, and the processing system. The output refers to the reports or records that the TPS generates.
The input is transaction data or transaction documents themselves, usually source documents obtained from the transactions that function as inputs for accounting systems. An example of this would be patron order slips or invoices.
The information processing system is the component responsible for processing functions breaking down the data contained within the inputs, transforming it into formats that computers can decipher.
- Input – A request for a product or a payment payable to an organization’s transaction processing system by a third party constitutes an input. Consequently, if your company uses batch processing, your Transaction Processing System will store and handle batches of inputs. Each input is managed in real-time if your company uses a real-time Transaction Processing System. Typical inputs include Bills, Coupons, Invoices, and Custom Orders.
- Output – Once the system has processed all the inputs, the system will generate the output documents. This may consist of receipts for record-keeping to verify a transaction or sale. In addition, they can be an essential data source for government-related reasons, such as tax. If a supplier submits an invoice to you, you can send the seller a payment confirmation once you have paid the invoice. The original invoice can be marked as “paid” in the company’s TPS.
- Storage – The storage aspect of TPS pertains to the placement of an organization’s input and output digital data or documents. However, some businesses keep these documents in an electronic database. Consequently, the storage component ensures that every document is organized, secure, and retrievable. If a supplier needs to confirm whether a particular invoice has been paid, the TPS can be searched for the invoice and verify whether or not payment was made.
- Processing – Responsible for reading each input and producing meaningful output. This process may also be utilized to specify input and output data. Consequently, processing times differ according to your company’s type of Transaction Processing System.
As TPS gathers data regarding transactions, it will also initiate processing, transforming it into business intelligence. The best examples include employee records, other transactions processed hotel reservations online transactions, and order processing.
Examples of the batch mode of processing transactions include check clearances process transactions and the generation of bills. Transaction processes in real time processing on-time will include microfinance loans, payment accounts and POS (point of sale) terminals.
TPS Features
Transaction processing retains the info necessary for collecting, altering data processing, or retrieving transactional data. Therefore, it has to be consistent and reliable to facilitate every transaction without problems. TPS can channel substantial levels of data.
This makes it indispensable in managing online business transactions. The system can handle large purchases by coordinating personal and banking details and shipping and processing orders from the right buyers.
TPS is also well suited to dealing with both security and hardware issues. It utilizes hardware and software components to handle large amounts of user and business data. However, security breaches can still occur since there will always be hostile parties who want to steal private information.
Therefore, a dependable TPS offers the latest security countermeasures to block data breaches or intrusions while safeguarding consumer information. Furthermore, if the terminal or network failure is, storage device operating system or terminal fails, it will be able to prevent user loss through the recovery of data integrity the latest OS (operating system) state.
Those who use transaction processing systems will have a greater capacity to offer improved market access. They can tap into multiple markets simultaneously and provide services or products to a larger audience, mainly if they utilize correct market penetration. Because TPS can work from anywhere, companies are no longer limited by language or geography.
Benefits of Using a Transaction Processing System
Some of the benefits of using a TPS are:
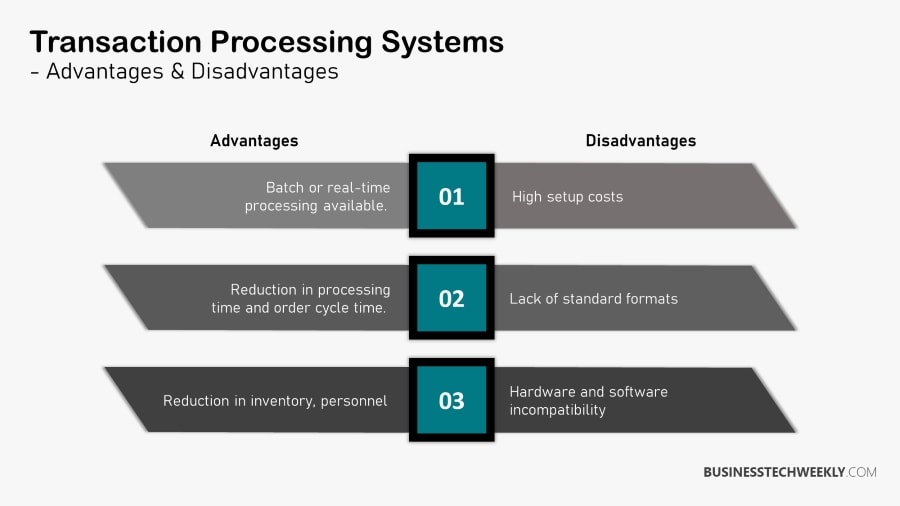
- Increased Transaction Speed – Businesses may expedite transactions and reduce client wait times using a TPS. The TPS employed determines the rate at which a business processes transactions. While some systems handle transactions promptly, others collect data over time and process it later, typically after business hours.
- Increased Cost-Effectiveness – A TPS may help a business save money by enhancing the cost-effectiveness of transactions and database data retention. A Transaction Processing System may arrange and manage thousands of transactions daily. This can save money for the organization by eliminating system upgrades or using several systems to satisfy demand.
- Improved Reliability – Using a TPS provides the exact and real-time confirmation of customer transactions. A trustworthy TPS can save your business money on future system issues and coding costs.
- Automated Management – TPS enables the bulk of an organization’s revenue management and internal resource to be automated. With the increase in automation, the TPS can reduce the time spent assessing transactions by people. Automation is essential for enhancing a business’s profitability since it allows employees to focus on more engaging tasks that demand critical thought.
Transaction Processing Limitations
TPS does have its limits. The records it provides are quite basic, which can become problematic for workers or managers who need to review a job carefully.
Although transactional processing is very intensive when entering or retrieving data, its calculations are not always accurate, and some of its other processing functions may seem rudimentary.
The effectiveness of TPS will depend mainly on the environment in which it is used.
Problems can also occur with the hardware or software since TPS combines input functions of the two. For this reason, virus attacks that succeed can be so debilitating since it targets the personal info contained within the database.
Any hardware malfunction might result system failure or in severe electrical damage, rendering the system useless.
TPS Databases
The database is a data collection that is organized. It provides rapid retrieval times, especially for non-structured requests that might be formed using a relational, database system, network, or hierarchical structures. With a relational structure, the database will organize the data using related tables. This provides greater flexibility.
The network will organize the data utilizing branches and nodes in a network structure. However, every child node might be linked to numerous elevated parent nodes.
Finally, hierarchical structures will organize that data into a collection of levels. It has a top-to-bottom form full of branches and nodes, and every child node will have branches that will link to a single elevated parent node.
Regardless of types of user friendly amount and types of transaction processing your database structure, they should all have optimal data placements. This allows the database to access data patterns from multiple users simultaneously and shorten transactions, allowing quick processing and high normalization while reducing redundant info to boost speed.
The historical data should always be archived, and the hardware should be well configured, allowing it to manage many multiple users simultaneously while providing rapid response times.
Conclusion
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) play a pivotal role in modern organizations by facilitating the efficient and accurate handling of daily operational transactions.
These systems are designed to process high volumes of routine transactions swiftly and reliably, ensuring data integrity and minimizing errors. TPS not only streamline business processes but also provide real-time insights into organizational activities, aiding decision-making and enabling timely responses.
From retail to finance, healthcare to manufacturing, TPS have become the backbone of industries across the globe, enabling businesses to maintain competitiveness, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve operational excellence.
As technology continues to evolve, the continuous refinement and integration of TPS will remain essential for organizations striving to achieve optimal performance and adaptability in today’s dynamic business landscape.


