Achieving Digital Resilience: 7 Steps to Building a Digitally Resilient Business

Organizational digital resilience is a critical element of modern-day commerce. Recent global events have wreaked havoc on businesses large and small, providing a stark reminder that digital technology can be susceptible to failure in the hour of need.
Business leaders need to consider what steps they should take in the event of a large-scale disruption. Here we provide guidance on building a digitally resilient organization, especially in such uncertain times.
Below are some tips for effectively accomplishing this.
On this page:
What is Digital Resilience?
As cybersecurity threats have grown over the past few years, the term “digital resilience” has gained momentum, but what does it mean?
Businesses realize that digital transformation depends on digital resilience to swiftly react to business disruptions through digital capabilities to restore corporate operations and profit on new conditions.
Becoming digitally resilient isn’t as simple as putting up a firewall or even adopting a zero-trust approach to protection. Digital resilience encapsulates the rapid convergence of:
- Cyber security and the protection of digital assets;
- Business continuity planning – an organization’s ability to sustain essential business functions in the event of an interruption; and
- Digital governance, risk and compliance (GRC) enables companies to keep digital machinery ‘on track’ and aligned with corporate objectives.

Digital Resilience vs Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity and digital resilience are not synonymous. Cybersecurity refers to the tactics and technologies that businesses use to defend against possible threats.
Increasing your business’s digital resilience is more about playing the long game and ensuring your organization is as secure as possible. It’s about anticipating and mitigating risk by constantly preparing the necessary resources, tools, and teams.
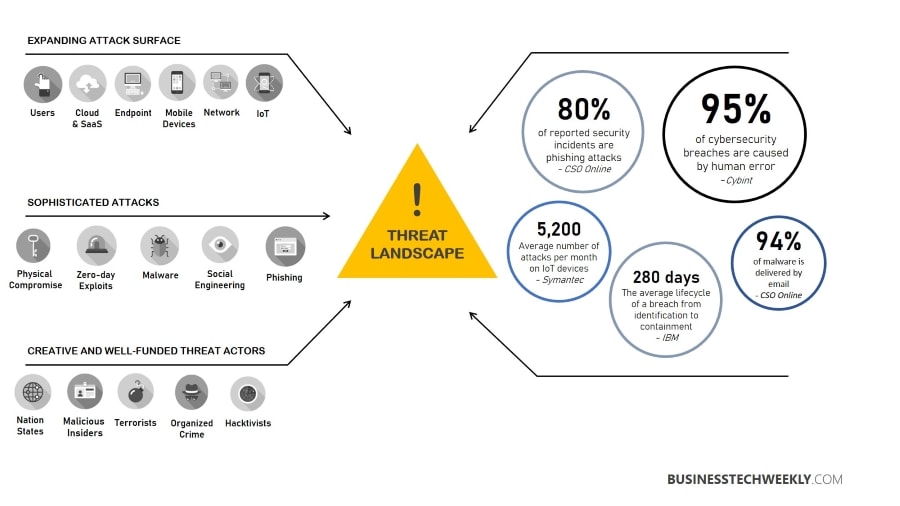
Why is Digital Resilience vital for Businesses?
Organizations are vulnerable to attacks. These attacks can come from hackers acquiring network access and then stealing or destroying sensitive data. In turn, this can severely disrupt ongoing operations, damage the enterprise’s reputation, and possibly lead to serious legal consequences.
Digital resilience is defined as the ability of an institution to continue its operations typically while detecting, preventing, containing and recovering from attacks on its IT or data infrastructure.
Digital resilience means more than just installing many security tools on computers and servers. It means making employees and managers more security conscious about cyber threats and reprimanding those who fail to comply.
7 Steps to Digital Resilience
With the recent market upheavals, companies recognized the importance of resilience in their digital processes, infrastructure, and apps to respond swiftly to disturbances.
Whether driven by market circumstances, legacy technology, or external threats like ransomware, built-in digital resilience is crucial to overcoming these obstacles.
Here are 7 steps that can help you achieve digital resilience within your business:
1. Ensure that cybersecurity is integrated into management and governance procedures – Cyber or technology risks is a complicated nonfinancial issue that can devastate a business’s bottom line and brand value.
As a result, businesses must include cybersecurity measures into their day-to-day operations and factor cybersecurity into strategic choices.
2. Establish a hierarchy of information assets and associated hazards – In many businesses, up to 50% of information assets are non-mission critical.
Businesses should inventory their information assets, compile a list of cyber threats, prioritize them, and focus their cybersecurity efforts on minimizing risks to critical assets. This can help them save up to 20% on cybersecurity costs.
3. Boost cybersecurity protection for critical assets – Vital assets should be safeguarded more vigorously than less vital ones.
Controls should include authentication, access rights, data loss protection, digital rights management, intrusion detection, and patching in addition to standard choices such as encryption.
4. Ensure that all staff are engaged – Each employee contributes to company security by engaging in activities such as exchanging sensitive information over secure channels rather than less secure channels such as email.
Phishing campaigns, cybersecurity exercises, and other initiatives will assist raise employee awareness of potential cyber threats and manage them.
5. Integrate security elements into information technology systems – Businesses should include robust cybersecurity controls into the heart of their information technology systems, much as a solid foundation must be established before constructing a house.
In-house software engineers should have the tools necessary to build less susceptible apps. Additionally, businesses should structure their information technology systems in ways that minimize their vulnerability to cyber threats.
6. Employ “active defences” to keep one step ahead of attackers – Eventually, hackers will target every business. Companies can more successfully resist hackers if they understand how they act.
Leading enterprises leverage big data analytics to spot indicators of potential attacks, such as efforts to connect into networks from odd places. Additionally, they keep current knowledge on cybercriminals’ skills and intentions and their identities in some cases.
7. Develop and test responses to cyber-attacks – Businesses should have procedures for responding to cyberattacks.
After establishing their incident response strategies, businesses should frequently put them to the test through simulated cyberattacks or “war games.”
Businesses have a complex problem of safeguarding their most critical data but not making it so difficult to access that their operations are slowed.
Attaining digital resilience will need the collaboration of a diverse range of stakeholders. To ensure that cybersecurity plans are rigorous and successful, board and senior management oversight are critical.
Dedicated cybersecurity teams must maintain a detailed and current awareness of the risks businesses face and design integrated defensive measures to counter them. Security procedures must be integrated into regular business activities by business units and the IT department.
Ten Digital Security Best Practices: Enhancing your Digital Resiliency
There are several ways for businesses to strengthen their resilience. They do not have to be expensive or time-consuming:
Gather information and take stock of your’ current state’
As organizations rely more on data (including personal information), privacy and cyber security will undoubtedly be reviewed. This entails mapping your whole organization’s data flow and comparing it to privacy and cyber security rules.
Strategize
Even if you believe you already see it. This requires an internal audit of all digital risk areas, preferably with external support.
Privacy and cyber security assessment are highly expected as organizations become increasingly reliant on data (including personal information). An evaluation of existing practises against privacy and cyber security regulations are required.
Also read: PCI DSS vs ISO 27001 vs Cyber Essentials
Master the security basics
No fancy security tool or approach will do you any good if you don’t master the basics. Employees and managers should become adept at installing access permissions, updates and patches.
While this might seem obvious, many companies are lackadaisical when it comes to enforcing it. Such an approach can result in them having to react to sudden attacks which could have been avoided.
Security must be data-centric
Digital security, which is data-centric, reinforces the traditional tactics used in the past. It does this through throttle access, encryption, automatic access decisions, tagging, segmentation, marking and tokenization.
When all these methods are employed simultaneously, data security becomes embedded in the way employees and managers handle critical assets.
Make sure your defense is proactive
Security automation and artificial intelligence can be used to detect intruders at a staggering speed. They will also be able to continually pressure test and monitor the environment to spot vulnerabilities long before you or human adversaries become aware of them.
Threat management must be fully leveraged to understand better enemies and the threats they represent. These methods will then encourage organizations to become hunters rather than the hunted.
Train personnel for digital resilience
Regardless of whether you believe you already have visibility into this. This requires completing an internal audit of all areas of digital risk, preferably with professional support.
As organizations become more reliant on data (including personal information), privacy and cyber security assessment are very sure to be required. This entails mapping your organization’s data flows and evaluating current procedures regarding applicable privacy and cyber security regulations.
Also see: Ten tips to improve Cyber Security Awareness amongst your employees
Test your organization’s responses to disruptions
Historically, most organizations understood the necessity to test responses to physical dangers like fire or equipment failure. However, in the digital era, most companies fail to assess their digital resilience.
Targeted testing, like penetration testing, is possible. A digital ‘fire drill’ can help determine how people, technology, and procedures are performed in a crisis.
Insure your risk
Since implementing the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), fines for privacy law violations have risen globally, and authorities take data protection seriously. Cyber assaults may cost a company millions of dollars.
Data breaches and privacy legislation violations, whether your fault or not, have negative reputational implications. Obtaining proper cyber and privacy insurance is recommended (and maybe required of your directors).
Take advantage of the cloud
The cloud will function as a secure shell. As such, organizations can take advantage of elastic workloads and multiple zone computing, making it far more challenging for enemies to locate and damage them.
Related: Using Cloud Computing to achieve Business Continuity
Continually review, revise and adapt
Digital resilience requires an adaptive mentality. To keep up with the changing market, start by focusing on strategic risks and regularly make minor updates, as needed, to respond to an evolving landscape.

Final Thoughts
Without a doubt, the next cyber attack will be unique from the last one. However, digital resilience is a continuous process that needs commitment and sustained attention. It does not come overnight or even over a year.
By incorporating digital resilience into every part of their information technology infrastructure, systems, and software, organizations can rapidly respond to changing market and customer demands and preserve competitive advantages.

