What is Internet Telephony?

Internet Telephony can be up to 60% cheaper compared to traditional analog phone systems. What’s more, internet telephony systems can be more reliable, scalable and flexible than their traditional counterparts.
In addition to cost savings, organizations can enjoy several further benefits by switching to an internet telephony service, including mobility, productivity, and scalability.
Below, we explain internet telephony, how it works, and some best practices for deploying an internet telephony system in your organization.
On this page:
Defining Internet Telephony
Internet telephony can be defined as the transmission of voice and data traffic, such as phone calls, fax, voicemail, and video over the internet using the Internet Protocol (IP).
In traditional analog systems, the same communication capabilities, except video, were transmitted over traditional analogue landlines.
How is Internet Telephony different from VoIP?
Commonly, internet telephony and VoIP refer to the same service, namely, the ability to make calls over the internet.
While the interchangeable use of these terms is generally acceptable, there is a difference between internet telephony and VoIP from a technical standpoint.
VoIP refers to the capability of transmitting and receiving voice traffic using the internet protocol (IP), hence the term VoIP (voice over IP). While also using IP, Internet telephony encompasses a broader range of communications, including voice and data such as fax and video.
Consequently, internet telephony can be considered to refer to a broader set of communications than VoIP.

Types of Internet Telephony Systems
Like their analog predecessors, Internet telephony systems required a PBX (Private Branch Exchange), which acts as the “brains” of any business telephony system to route and connect calls to and from the public telecommunications network (known as the public switched telephone network, or PSTN).
Related: What is a PBX?
Modern PBXs also use the internet protocol and are often referred to as IP-PBX. When choosing an Internet Telephony system, you have two choices:
- On-Premises – On-premise IP telephony deployments require the IP PBX associated components to be located on-site, typically at the same location as where they are used. The hardware and equipment (including any servers, desk phones) are connected to the business network.
The main advantage of an on-premise internet telephony system is that you retain maximum control over the platform.
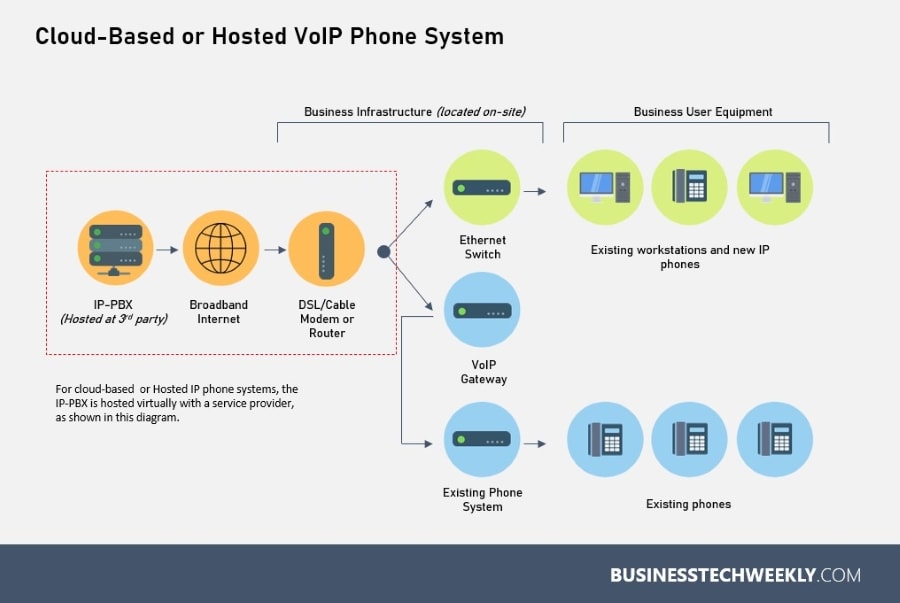
- Hosted or Cloud-Based – In contrast, in a hosted (also referred to as virtual) IP PBX telephony solution, the IP-PBX is located at a site owned and operated by a third party or an internet telephony service provider. The only equipment required on-site is IP desk phones and a few connectivity components.
A cloud-deployed IP telephony solution is set up the same way as a hosted solution. The only difference is that cloud internet telephony is provided as a managed service, covering maintenance, upgrades, and day-to-day management and administration of the solution.
Should I choose a cloud-based or an on-premises IP Telephone Solution?
On-premise solutions offer you complete control over your system. However, if you do not have a third party maintenance agreement, you will need some technical resources to manage your IP telephony system.
The same is also true for hosted solutions. While the service provider may take care of the maintenance for the underlying hardware, you will still need to have access to resources to manage and administrate (adding and removing extensions, users, system updates, etc.) the telephony solution on a day-to-day basis.
Consequently, on-premise and hosted solutions are ideal for organizations with expertise and resources to manage such systems.
In contrast, you only require a robust internet connection for a cloud-based telephony solution, which most organizations already have. Moreover, as a managed service, typically provided as a monthly subscription on a per-user basis, cloud systems are ideal for SoHo, small, startup businesses.
How does Internet Telephony work?
When you speak into a laptop, mobile or headset microphone, your voice is digitized and sent over the Internet to the recipient.
The audio signal, i.e. your voice, is split into uniquely labeled data packets. Each data packet travels independently over the internet and is reassembled in the correct order at the destination. The reassembled data is then converted into audio and heard by the recipient.
To use an internet telephone, you need an internet telephony service provider and the correct hardware and software.
You get a virtual server from your service providers, and all the incoming calls are connected with it. The VoIP service provider converts this call to an audio file and transmits it to the IP phone. Now, you’ll be connected with a caller as usual. The only difference is you’re using the internet for transmission instead of a cell tower.
Internet Telephony Requirements
Network Bandwidth
You can use internet telephony (VoIP) if you have a high-speed broadband connection. The good news is that VoIP telephony does not consume as much bandwidth as you may believe.
It would be best to plan on using 100 Kbps (or 0.1 Mbps) per voice service line. For example, if you plan on using ten phone lines, you will require 1000 kbps (1 Mbps) for your network.
Ideally, you should aim to use 80% of your available network bandwidth. A clogged network might lead to poor-quality phone calls.
See also: How to Increase Bandwidth Performance
Low Latency
Your internet telephony experience is enhanced if you’re internet connection is reliable. This is because the faster data travels over the internet, the better your connection.
Monitoring “Jitter” and “Ping”, which can help measure the reliability and consistency of your connection, will help you assess the quality of your network.
Ping and Jitter in successful VoIP deployments are fewer than 70 ms (milliseconds). Take the free speed test to determine how fast and stable your network connection is.

Wired over WiFi
You should aim to use a wired Ethernet connection for your internet telephony whenever possible. Wireless internet (WiFi) may be functional for some users, but it is not as dependable as a wired connection.
You may want to consider investing in a Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch for users who work in an office. Over a single line, PoE switches provide data and power to VoIP phones.
Data Prioritization
You can’t always predict every network scenario, but you can prepare for increased load. Software upgrades, file transfers, and watching YouTube videos are examples of high-traffic activities.
Setting up VoIP Quality of Service (QoS) on your router will allow you to optimize network voice traffic. Your internet telephony service provider can advise on recommended QoS changes for their network.
How much does Internet Telephony cost?
Most vendors provide a range of packages to cater for your business’ demand. Typically, the packages are segregated into three tiers:
Basic IP Systems
A basic internet telephony package would consist of a cloud-based VoIP subscription. You can expect to such packages to start from $20 per user per month. Such a system would likely offer free number porting, a local or toll-free phone number, and unlimited calling.
Auto-attendant, hold music, and free online faxing are also likely to be included in basic packages, although this may vary between vendors.
Mid-range Internet Telephony Package
All of the aforementioned features, along with text messaging and unlimited conference calls, can be expected to be included with mid-range VoIP systems.
Some providers may also provide an app, allowing you to make and receive calls on a mobile device.
Enterprise-grade VoIP Solutions
All features from the basic and mid-range, as well as call recording, voicemail to text, and voice analytics, are available with enterprise VoIP systems.
Enterprise-grade VoIP solutions are heavily tailored for organizations. Therefore, the pricing and cost savings for corporate VoIP systems are determined by your firm’s size and your overall requirements.

