Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Comparison of Leading Cloud Platforms

Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Cloud computing has become a key driving force for businesses across industries today as more and more companies shift their applications from on-premises data centers to the cloud in an attempt to improve flexibility and scalability and reduce costs.
The cloud computing market is flooded with a large number of providers with different services and features to suit companies with varying budgets, requirements, business models, and sizes. However, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud are the biggest players in the IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) market.
These three big public cloud vendors have successfully resolved the early problems associated with data integrity and security by offering flexible, safe, reliable cloud services and state-of-the-art features. However, it is important to note that these platforms differ in several ways. Each of them offers a varied set of features, and one of them may suit your business model more than others.
To make it easy to select the best cloud computing platform, we present a detailed comparison of these three cloud services in terms of their features and offerings, performance, pricing, pros, and cons. Read on to learn more about Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud and understand how they compare with each other to be able to make an informed decision.
On this page:
- Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure Comparison Overview
- Strengths and Weaknesses
- Establishment
- Availability Zones
- Market Share
- Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Comparison of Basic Features
- Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: How do they compare in Pricing?
- Discount Programs
- Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Core Differences
- Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Which is Best for You?
Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure Comparison Overview
When using an IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), a third-party provider hosts and maintains the core infrastructure including software, hardware, storage, and servers on behalf of the customers. The applications are hosted in a scalable environment and the customer is charged on a usage basis.
While there are several options available in the market, selecting the right cloud platform is crucial for the business. It is natural to have questions about how to choose the provider that meets your budget and needs. Here are some key considerations that should guide your comparison and decision.
- Reliability: It is imperative to go beyond recognition and reputation and focus on feedback from real users.
- Pricing: A comparison of the cost of running an on-premise server and the resources of a cloud platform should help.
- Stability: Take into consideration the consistency of performance, updates, load balancing, and dispersed platforms.
- Standardized Service: Check whether the provider offers cost-effective packages of applications and resources you need. Bundled services can save you a lot as compared to individual services and products.
- Flexibility: You certainly want to join a flexible cloud computing platform that supports your organization’s growth and scalability.
Google Cloud Platform, though relatively new in the area of IaaS, has managed to make a place among the leaders. It provides support for Windows and Linux servers up to 2016 versions. It has about 20 regions divided into availability zones across the world.
Google is a pioneer in undersea server deployment and has a cabling system starting in Guam and connecting servers across Asia, Japan, United States, South Pacific, and Australia. GCP services are also quite simple to set up and configure.
Some of the key services offered by GCP include app development, productivity tools, AI and business analytics, data storage, and management. If your organization uses Google products, they link naturally, making it an ideal option.
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a robust cloud computing platform known for its vast toolset with impressive breadth and depth of services. It was established in 2006 and currently offers services like SaaS, IaaS, PaaS, and more across availability zones and regions.
Availability zones are kept far from one another to ensure there is a minimal lapse in service in instances of disaster. AWS is a highly preferred solution among enterprises because it not only works across operating systems but offers impressive performance and features. It uses serverless computing to handle infrastructure management, allowing you to focus on more important tasks.
The vendor offers more than 18,000 services including productivity tools, storage solutions and databases, developer and management tools, data computing and app integration, predictive analysis, and machine learning.
Azure from Microsoft is a popular choice in the cloud computing space excelling at app deployment, flexibility, and features. It offers a robust IaaS platform for companies across sectors and with varying sizes and needs. Its compatibility with Linux containers and virtual guest operating systems is one thing that differentiates it from other cloud platforms.
Microsoft Azure also comes with ready-to-run server apps supporting a variety of languages including Java, .Net, Python, Node.js, and PHP. The platform serves in more than 60 regions worldwide and is the easiest to configure and use. It uses the latest technology to pass cost-saving and productivity boost to its customers.
Some of the services you can enjoy with Azure include blockchain technology, app and game development, big data and predictive analysis, scalable data warehousing, and IoT integration.
The platform has more than 200 products to help organizations in any scenario. If your organization uses Microsoft tools and services, Azure’s natural linking facility makes it the perfect choice.
Strengths and Weaknesses
There is no ‘one size fits all’ solution to cloud computing as the requirements vary between businesses as well as projects.
Let us try to understand the advantages and limitations of the three cloud vendors.
Google Cloud Pros and Cons
Google has a dominant presence in the open-source community and appeals to enterprises that are into analytics, big data, and machine learning. As it has developed the Kubernetes standard currently offered by other platforms, it excels at containers. It also supports load balancing and does well at offering fast response times.
Google Cloud lacks IoT features, file transfer, storage options and compute services. Users also report difficulties migrating and deploying on the platform. It struggles to acquire enterprise customers and is third in the market share. However, it is rapidly developing both its data centers and its offerings to overcome its limitations and improve adoption rates.
It is also worth noting that Google has the lowest presence among the three cloud platforms and is not present in one of the biggest markets of the world, China. Azure and AWS, on the other hand, are present in mainland China.
AWS Pros and Cons
The biggest strength of Amazon is its dominance in the market. The massive scope of its operations is one reason for this popularity and adoption. AWS has remained a market share leader in the cloud landscape for over 10 years with its platform configuration options, security, policy features, reliability, and more. It boasts a huge and growing array of services and a comprehensive network of data centers.
Amazon’s weaknesses relate to its complex pricing structure which is a concern for many clients. Though it offers low prices, many organizations find it difficult to understand its price model and manage costs effectively when working with huge volumes.
Moreover, despite such a wide array of features, scalability can be difficult, so some organizations may not opt for this platform as they constantly expand in industries like finance and healthcare.
Though the availability of such a large number of features is a benefit, it can sometimes be difficult for users to navigate through them.
Azure Pros and Cons
Though Microsoft entered the landscape late, it got a jump start by taking its on-premise software and repurposing them for the cloud.
A big reason for Azure’s success is its ease of deployment for organizations that already use Microsoft tools and systems like .Net, Active Directory, System Center, Windows Server, and more. This builds trust and loyalty among existing customers. Such users also receive discounted prices for these services.
Another advantage of Azure is its increasing advancement with open-source technologies. Presently, more than half of the company’s tasks are run on Linux.
Talking about the downsides, Azure has reported several outages over the years, including the big 2019 global outage. There are many dissatisfied customers in terms of technical support, training, and documentation. Its service experience does not meet the expectations considering its long existence as an enterprise provider.
Establishment
Google Cloud
Run by Google, the GCP is a cloud computing services suite based on the same infrastructure that Google uses for its internal products like YouTube, Google Search, and more.
It was established in 2011 and has since then created a prominent presence in the industry. The intent behind its establishment was to strengthen the offerings of Google.
However, today, it offers enterprises services that enable using the platform sharing the same infrastructure as YouTube and Search.
AWS
Amazon Web Services is an Amazon subsidiary that caters to users with a pay-as-you-go cloud computing service for personal, business, and government applications.
As the most experienced player in the industry, AWS has established a greater trust, reliability, and user base than others.
Azure
Microsoft Azure or simply Azure was introduced in 2010 to provide a cloud computing platform to businesses.
Right from its inception, this Microsoft platform has experienced rapid growth in the industry.
Availability Zones
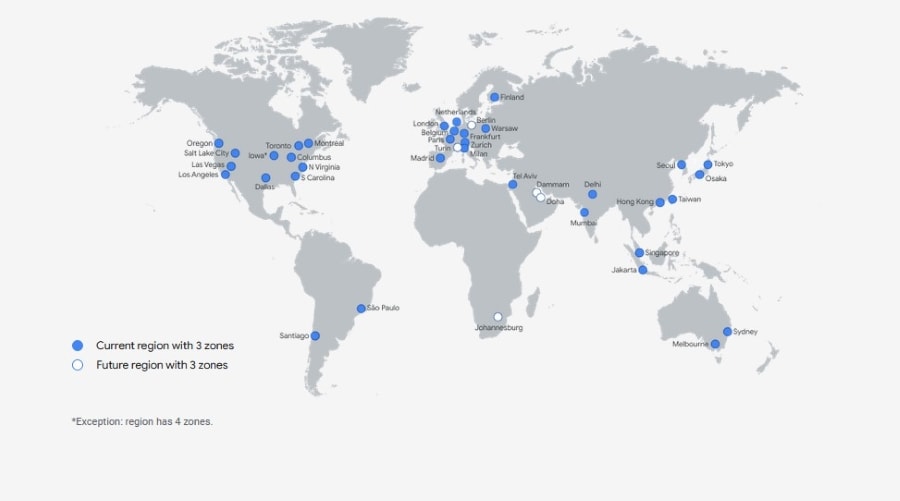
As Amazon Web Services is the oldest player in the landscape, they certainly had more time to establish and expand the network.
This is why AWS offers hosting services in several locations around the world. Azure and Google Cloud also host in multiple locations globally but the difference lies in the number of their availability zones.
AWS has 66 availability zones and will be having 12 more shortly. Azure serves across 140 countries of the world and has 54 zones.
Google Cloud, on the other hand, is available in 20 regions worldwide and will operate in 3 more regions in the future.
GCP Availability Zones
AWS Availability Zones
Azure Availability Zones
Choosing an Availability Zone
Before selecting a supplier, consider where your organization does business and how it conducts business. When choosing a cloud service, consider the following questions:
- Where does your organization operate?
- Can data for distant offices be maintained in a single location, or must it be shared across offices across regions?
- Will data have to be transferred from one zone to another?
- Are data retrieval and processing times critical?
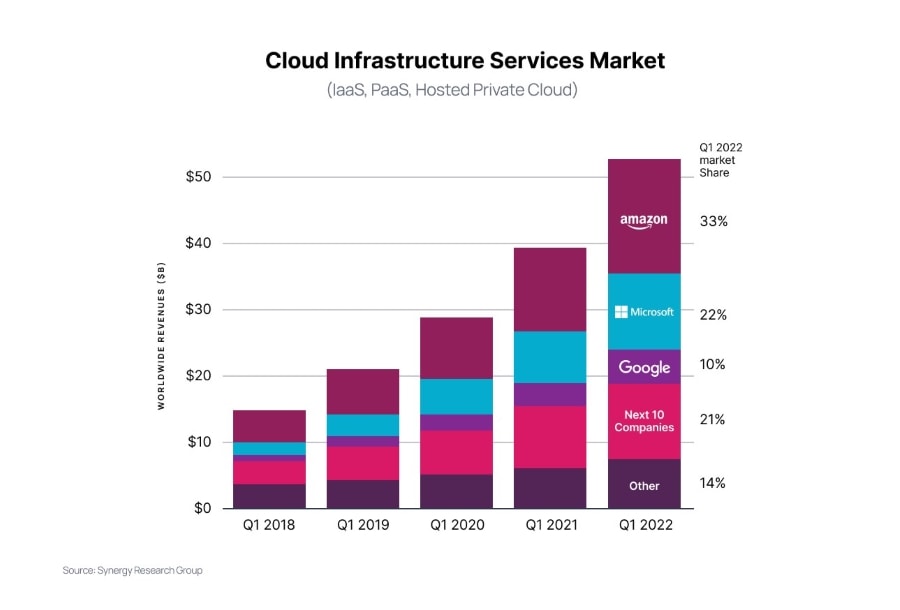
Amazon has been dominating the cloud computing landscape ever since its inception with a global market share of 32 percent. The second leading vendor in the global marketplace is Microsoft Azure with 19 percent while Google Cloud Platform holds a market share of 10 percent.
AWS has reported a revenue of $13.5 billion for the first quarter of 2021 demonstrating a 32% growth compared to $10.33 billion in 2020.
Microsoft does not disclose the revenue but reports revenue growth of 50% over the previous quarter. On the other hand, Google Cloud reported revenue of $4.05 billion in this quarter, a 46% increase from last year.
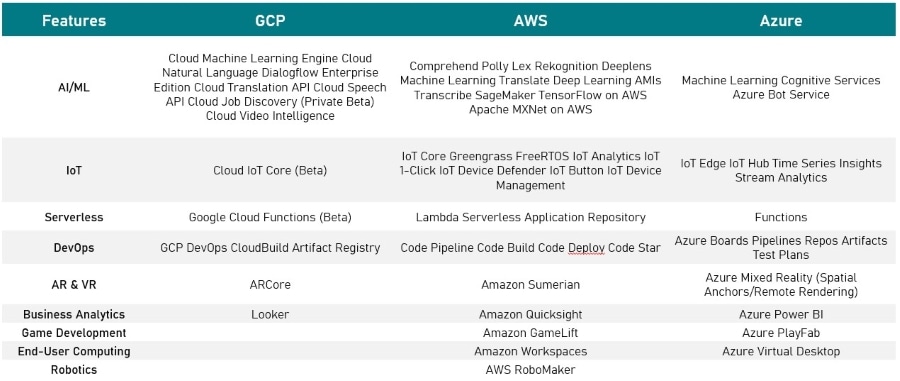
Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Comparison of Basic Features
All three cloud computing platforms provide various compute services such as virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing.
Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Summary of Features
Each platform has different features and capabilities, and users should consider their specific needs when choosing a platform.
By comparing the basic features of compute services, storage services, and networking services for each platform, users can determine which one is best suited for their requirements.
Compute
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have a similar range of product offerings. Whenever a platform introduces a new product, the competitors also release comparable products in a short time under different names.
However, the differentiating factor between these products is the way the product interacts with other services within the portfolio.
Google Cloud
Comparing the compute with others, Google has a shorter range of services than its competitors. The primary service is Compute Engine offering a plethora of features including Windows and Linux operating system support, predefined and custom machine types, auto-discounts, per-second billing method, and green infrastructure that saves energy as compared to traditional data centers. It also has a free tier that includes an instance for up to 12 months.
Like other cloud providers, Google is set up to offer several microservices and containers. It offers the Kubernetes engine to organizations for container deployment. What gives Google an edge in this area is its heavy involvement in the Kubernetes project.
AWS
Amazon’s flagship compute offering is EC2(Elastic Compute Cloud). This service offers several exciting features including support for Linux and Windows, a number of instances, GPU instances, bare metal instances, auto-scaling, high-performance computing, and more. The free tier of EC2 provides 750 hours of usage for up to 12 months.
The container services within Amazon’s compute are getting increasingly popular with a variety of options including Docker, Kubernetes, and Fargate service that automates cluster and server management with the use of containers. There is also a virtual private cloud option called Lightsail, Elastic Beanstalk for scaling web applications, and Batch for batch processing.
Azure
The primary compute service of Microsoft is Virtual Machines based on an open-source platform compatible with Windows and SQL Server, IBM, Oracle, Linux, and SAP and comes with integrated support for Microsoft software and hybrid cloud capabilities. It offers a wide range of solutions like testing, development, and app deployment.
Azure’s container service is based on Kubernetes and it uses Container Registry for Management and Docker Hub. It also supports Batch service and cloud service that facilitates scalable web application. There is also a unique feature called Service Fabric designed specifically for applications microservices architecture.
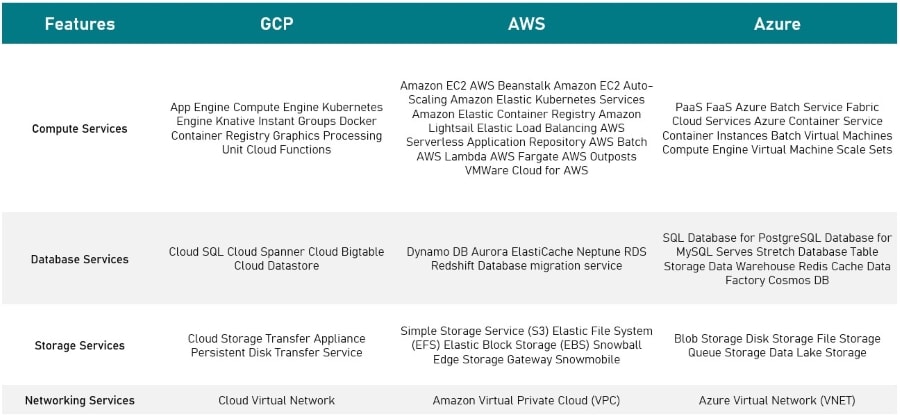
Here is a detailed comparison of the compute services of the three platforms:
| Vendor | Compute Services |
| Azure | Azure Container Service
Virtual Machines Batch Container Instances Service Fabric Cloud Services |
| AWS | Elastic Compute Cloud
Elastic Container Service Elastic Container Registry Batch Lightsail Auto Scaling Elastic Load Balancing Fargate Elastic Beanstalk |
| Google Cloud | Kubernetes
Container Security Compute Engine App Engine Functions Knative |
Storage
Cloud platforms offer extensive storage capabilities as one of their primary benefits. All three providers have a variety of databases and backup plans on offer.
AWS provides users a wide range of storage options while Azure excels at specialized solutions for storage and backup.
Google, on the other hand, offers fewer storage options as compared to the other two but adopts a more focused approach.
Google Cloud
Google offers users basic cloud storage which is their Unified Object Service. It also has a Persistent Disk option. Just like Amazon’s Snowball, Google has a Transfer Appliance in addition to online transfer services.
Coming to the database, Google Cloud has both – the SQL-based Cloud SQL and a relational database named Cloud Spanner. It also has two NoSQL options – Cloud Datastore and Cloud Bigtable. There is no backup or archive service available.
AWS
Primary storage services for AWS include the Simple Storage Service for object storage, Elastic Block Storage for persistent block storage, and Elastic File System for file storage. There is also a Storage Gateway that facilitates a hybrid storage environment and a physical hardware storage device called Snowball to transfer petabytes of data in cases where internet connectivity is not available.
Talking about the databases, Amazon supports several SQL-based databases, the ElastiCache feature for in-memory storage, and a data migration service. The backup feature called Glacier is available at low rates while the Storage Gateway facilitates easy backup and archiving.
Azure
The primary storage service is Blob Storage for REST-based unstructured data. It uses Queue Storage for big-volume workloads and supports Disk Storage and File Storage. There is also Data Lake Store for big data applications.
The database options available for Azure are quite extensive. It offers three SQL options – SQL database, a database for MySQL, and a database for PostgreSQL. It also has a hybrid Server Stretch database offering on and off-premise storage for companies using Microsoft SQL server. They offer backup services along with archive and site recovery.
Here is a detailed comparison of the storage capabilities offered by the three platforms:
| Vendor | Storage Services | Database Services | Backup Services |
| Google Cloud | Cloud Storage
Persistent Storage Transfer Service Transfer Appliance |
Cloud SQL
Cloud Spanner Cloud Bigtable Cloud Datastore |
None |
| AWS | S3 (Simple Storage Service)
EFS (Elastic File System) EBS (Elastic Block Storage) Snowball Storage Gateway Snowmobile |
RDS
Aurora Redshift ElastiCache DynamoDB Neptune Database Migration Service |
Glacier |
| Azure | Blob Storage
File Storage Disk Storage Queue Storage Data Lake Storage |
SQL Database
Database for MySQL Redis Cache Data Factory Cosmos DB Table Storage Server Stretch Database Database for PostgreSQL |
Backup Archive Site Recovery |
All three platforms provide access to some powerful analytical tools. AWS has launched a breakthrough analytics service called Quick Sight. It includes ready-to-use templates and the service is quite affordable as compared to other traditional solutions. Microsoft Azure has also improved its machine learning tools and analytics over the years and even introduced the Data Lake Analytics system.
Google focuses on Big Data analytics and offers a special area under its cloud offerings. With these tools, APIs for Speech, Vision, and Translate can be easily integrated with third-party resources.
Network Services
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all offer a network of interconnected data centers to facilitate networking capabilities with high fault tolerance and minimum latency. Users can leverage these services to launch computing resources in a secure environment and connect them to other cloud services, either running on-premise or on the cloud.
With each of these cloud providers, customers can enjoy the ability to control the networking environment. In this regard, these providers have more similarities than differences. However, a key differentiator is the organization’s proximity to the data center location, a factor that affects costs, latency, redundancy options, and disaster tolerances.
Let us take a look at the networking services offered by these vendors:
| Service | Azure | AWS | Google Cloud |
| Virtual Network | Virtual Networks | Virtual Private Cloud | Google Virtual Private Networks |
| DNS | DNS Traffic Manager |
Amazon Route 53 | Google Cloud DNS |
| Peering | ExpressRoute | Direct Connect | Google Cloud Interconnect |
| Load Balancing | Azure Load Balancer
Application Gateway |
Elastic Load Balancing | Cloud Load Balancer |
| Global Content Delivery Networks | Content Delivery Network | Amazon CloudFront | Google Content Delivery Network |
Hybrid Options
One of the latest growing trends among large public cloud platforms is the focus on fulfilling the hybrid and multi-cloud needs of users.
The hybrid approach is specifically relevant where customers deploy across multiple infrastructures from different vendors and also want to maintain some applications on-premise.
Leading cloud providers have taken significant steps to respond to these customers who are not yet ready to adopt all-cloud which comprise a majority of enterprises.
Among the three competitors, Microsoft has long been recognized as the perfect option for those who go with this method. Azure provides to its users the software and hardware needed to deploy the cloud services on a local data center with a shared code, management portal, and API for ease of integration and operation.
AWS signaled its transition to a hybrid approach back in 2018 with the launch of Outposts, a fully-controlled service where the provider gives pre-configured racks to premises to run AWS services like they were a part of the data center.
Later, in 2019, Google also made its move in the direction with Anthos, a rebranded cloud platform that combines existing Kubernetes Engine, Anthos Config management, and GKE On-Prem to provide a unified platform for security, policies, and administration across hybrid deployments.
Security
The cloud offers several benefits to enterprises in terms of scalability and flexibility but a cloud environment may also develop significant risks that were previously not present in on-premise systems. Cloud platforms offer various security features to help customers establish and maintain strong security.
AWS uses Fortinet to provide security solutions to Virtual Private Networks on an on-demand basis in several zones. Fortinet also supplies data and application security to Azure users and eliminates additional security expenditures during migration.
Talking about the Google Cloud Platform, it relies on a powerful firewall product from FortiGate for advanced security. Let us look at the differences between these three providers in terms of security.
| Security Service | Azure | AWS | Google Cloud |
| Web Firewall | Firewall, Application Gateway | Web Application Firewall | Firewall Insights |
| Authentication and Authorization | Active Directory | Identity and Access Management | Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy,
Cloud IAM |
| Security Assessment | Security Center | AWS Security Hub, Amazon Inspector, | Cloud Security Command Center |
| Identity Management | Active Directory B2C | Cognito | |
| Threat Detection and Monitoring | Advanced Threat Detection | Amazon GuardDuty | Cloud Armor |
| Protection with Data Encryption | Storage Service Encryption | Key Management Service |
Compliance Certifications
Microsoft and Google are known to lead when it comes to the security of cloud information storage.
All three platforms offer various compliance certifications that demonstrate their commitment to security and data privacy.
Azure and Google Cloud conduct their security policy that complies with the regulatory standards of the ISO, GDPR, CSA STAR, and HIPPA.
- Google Cloud is certified for a range of compliance standards, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA. It also provides compliance reports and third-party audit reports.
- AWS is certified for a range of compliance standards, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA. It also provides compliance reports and third-party audit reports.
- Azure is certified for a range of compliance standards, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA. It also provides compliance reports and third-party audit reports.
The level of security offered by Azure is the highest among the three providers. It complies with over 90 quality benchmarks across 50 regions worldwide.
Data Residency and Sovereignty
All three platforms allow users to choose where their data is stored and provide options for data sovereignty.
Key Tools
Experts suggest that new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, artificial intelligence, and serverless computing are key factors differentiating cloud services from one another.
Google Cloud, Azure, and AWS have all begun experimenting with features in these areas and are likely to add functionality in coming years.
Let us take a look at the key cloud tools each of these vendors are working on:
Google Cloud
- Artificial Intelligence – The platform focuses a lot on machine learning and artificial intelligence. The open-source library called TensorFlow facilitates building machine learning apps. It is a highly regarded library that makes Google a leader in artificial intelligence development.
- IoT and Serverless – Google Cloud excels at API offerings for translation, speech, language, and more. It also offers serverless and IoT services but they are still in their testing stages.
AWS
- AI and ML – Among other tools, AWS offers an AI-based camera for the development and deployment of machine learning algorithms, DeepLens. AWS has also introduced Gluon, an open-source library intended to help developers and novices alike to build and customize neural networks without any knowledge of AI programming.
- Serverless – Just like other areas, AWS offers several services in the latest technologies. Some of these include SageMaker for the deployment of machine learning models, Greengrass IoT messaging, Lex interface that supports Alexa, and Lambda serverless computing.
Azure
- Cognitive Services – Microsoft puts a lot of resources on AI and offers a machine learning service on Azure. It also offers Cognitive Services that include APIs for Text Analytics, Computer Vision, Bing web search, and more. Azure even has serverless computing and management and analytics tools for IoT.
- MSFT Software – Some of the most popular tools focus on supporting on-premise Microsoft software. Azure Backup and Visual Studio Team Services are examples of top Microsoft tools.
Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: How do they compare in Pricing?
When it comes to selecting a cloud service provider, pricing is a prime factor influencing the decision in enterprises. Price is also a big attraction for those who consider shifting to the cloud, particularly as the fierce competition has resulted in a downward trend for prices. However, understanding pricing between the three leaders is challenging.
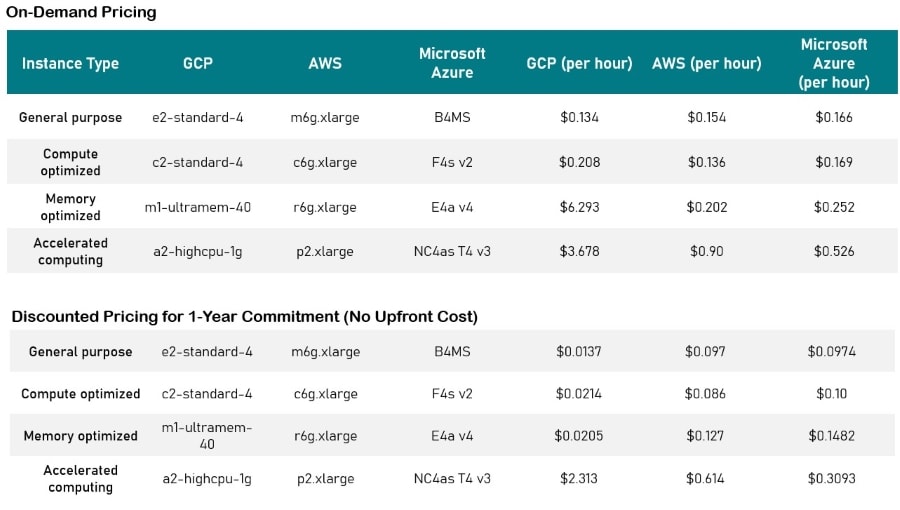
All three players offer different pricing models, discounts, and price slashes from time to time, making it difficult to make a direct comparison to find out the clear winner.
Prices can also vary at the enterprise level as customers can negotiate discounts with the sales representatives.
Free Tier
All three platforms offer a free tier with limited resources to help users get started with their services.
- Google Cloud’s free tier includes 28 products, including virtual machines, storage, and machine learning services, with a usage limit of $300 for the first 12 months.
- AWS’s free tier includes more than 60 products, including compute, storage, and machine learning services, with a usage limit of 750 hours of Amazon EC2 per month for the first 12 months.
- Azure’s free tier includes more than 25 products, including virtual machines, storage, and machine learning services, with a usage limit of $200 for the first 30 days.
Payment Options
All three platforms provide multiple payment options for users to choose from.
- Google Cloud accepts payment via credit card, bank transfer, and checks. It also allows users to set up monthly invoicing for their accounts.
- AWS accepts payment via credit card, bank transfer, and checks. It also offers an AWS Billing and Cost Management Console to help users manage their billing and payment.
- Azure accepts payment via credit card, bank transfer, and checks. It also provides an Azure Cost Management and Billing Console to help users manage their billing and payment.
Google Cloud
Google, unlike Microsoft and Amazon, intends to offer a friendly pricing structure that differentiates it from others. It tries to beat the prices of other providers with flexible plans and deep discounts.
Google Cloud offers the most basic instance among the three providers. This instance covers 2 CPUs and offers 8GB of RAM at about $52 per month which is 25% cheaper than the other two.
The largest instance from Google costs about $5.32 per hour including 160 virtual CPUs and 3.75TB of RAM. AWS and Azure offer pay-per-minute billing options while the Google Cloud offers a pay-per-second billing model that helps users save more money as compared to others.
Google also allows saving with different discounts and flexible contracts. All three vendors offer introductory price tiers to let customers try their services before buying and also have permanent free tiers with limited features.
AWS
Amazon doesn’t keep things simple either. The provider offers a cost calculator to estimate the prices but it is difficult to get an accurate cost because of the large number of variables involved.
The smallest instance costs about $70 per month and includes 2 virtual CPUs and 8GB of RAM. With the largest instance, you get support for 128 CPUs and 3.84TB of RAM for about $4 per hour.
Azure
Microsoft has a complex pricing structure. It is difficult to comprehend the price structure without using third-party tools and services as the software licensing options are not straightforward.
Azure also offers complicated discount programs that further add to the difficulty of estimating costs. Azure’s smallest instance costs about $70 per month for 8GB of RAM and 2 virtual CPUs.
The largest instance covering 128 virtual CPUs and 3.89TB of RAM is priced at about $6.79 per hour.
Discount Programs
Price comparison between Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud seems to be meaningful only for a short time because of frequently changing prices, newly launched products, and a choice of discount programs.
However, it is a good idea to compare different discount options from each vendor to achieve cost savings for the services offered.
Google Cloud
Google also has two primary discount programs – Sustained Use Discounts (SUDs) and Committed Use Discounts (CUDs). While CUDs cover fewer services as compared to AWS services, they compete neck to neck with Amazon’s Reserved Instances as the discounts are bigger and don’t require an upfront payment.
Moreover, these discount programs apply to customizable Virtual Machines service, thereby providing flexibility based on the customers’ unique usage and memory needs.
The SUDs are discount programs that apply automatically when Google Cloud services run over 25% of the month. The program rewards such customers with high levels of service usage because the higher the usage during the month, the greater are the discounts.
These programs are ideal for customers who are not sure whether committed use discounts will work for them.
AWS
Amazon Web Services has introduced two discount programs – Savings Plans and Reserved Instances.
The difference between the two is that Reserved Instances works against on-demand pricing based on the commitment of usage while Savings Plans offer discounts based on committed spending.
Some of the services covered under Savings Plans include Lambda, Fargate, and EC2 while Reserved Instances include DynamoDB, Redshift, RDS, EC2, Elastisearch, and more. AWS can be expected to extend the programs to include more services in the future.
Azure
Microsoft Azure offers a discount program named ‘Reservations’ or Azure Reserved VM Instances to let users cut costs by committing to a fixed usage period of 1 or 3 years. You can pay monthly or upfront without losing discount benefits.
This program is quite popular among CloudHealth customers though there are 15 types of services to choose from, including storage, database, data, and analytics.
Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Core Differences
Below is a summary of the key differences between the three leading cloud providers:
| Vendor | Advantages | Limitations |
|
Azure |
· Second largest provider
· Hybrid cloud · Open-source support · Wide array of features · Integration with Microsoft tools |
· Documentation issues
· Incomplete management tools |
|
AWS |
· Dominant position
· Mature offerings · Extensive training · Support for large organizations · Global reach |
· Cost management
· Too many options · Difficulty setting up |
|
Google Cloud |
· Ideal for cloud-native systems
· Great discounts and flexible price models · Support for portability |
· Smaller array of features
· Not enterprise focused · Late entry into the market |
Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure: Which is Best for You?
As stated earlier, the best public cloud vendor for you depends on your business model and requirements. The choice of a cloud provider can even vary between projects within a business.
Experts believe that the clear winner is a multi-cloud strategy that offers better features and services and reduces lock-in risks. Azure, AWS as well as Google Cloud offer pay-as-you-go pricing, excellent support, a free tier, and security features.
Here are some guidelines you can consider to make it easy selecting the best cloud provider for different use cases.
- Azure: Go with Microsoft if you are interested in hybrid options. Your Server environment will readily connect to the cloud platform and your existing .Net code will continue working, making your migration to the cloud easy and hassle-free. Azure is considered ideal for start-ups and developers.
- AWS: Select Amazon Web Services if you have a large company. It offers a wide range of functionality with a rich selection of tools and a great global reach. AWS is not a good option for smaller businesses looking for a close relationship with the vendor.
- Google Cloud: Google is working quickly on its cloud platform and is an ideal pick for those who value innovation. The platform is built on its key strength which is machine learning. It also tries to overcome limitations by partnering with Cisco which has experience with enterprise offerings. So, if you are looking for a green solution or a comprehensive container-based model, Google Cloud is the right selection.
Conclusion
The cloud platform is the base on which your business applications run. It should, therefore, ensure a secure environment for infrastructure development, offer 24*7 support, cost-saving, and automatic updates. A comparison of cloud services can help you find the right vendor that suits your budget and business needs.
While AWS continues to lead the market with its extensive functionality, Microsoft has started making efforts to shorten the gap with its continuous investment in the Azure cloud platform. For organizations that rely a lot on Microsoft for skills and technology, Azure definitely continues to be the ideal option.
If you run a small, web-based start-up and looking to scale quickly, you should give Google Cloud a try. And if you are in search of a provider with a huge array of services and wide reach, AWS is probably the best choice for you.
Organizations can even select services from different vendors and create a multi-cloud environment to make sure their security, performance, and financial goals are achieved.

