Private Cloud vs Public Cloud: Which Cloud Computing deployment model is best for your business?
Across the globe, cloud computing is growing exponentially. Businesses, small, medium and large, are harnessing its benefits and leveraging cloud technologies across their organization. But with a number of cloud deployment methods available, private vs public vs hybrid cloud, which cloud service delivery should you choose for your business? When comparing private vs public and even vs hybrid cloud, each model presents a different value proposition. Your choice will depend on factors relating to use cases and their drawbacks. What may be right for some businesses may not be the right model for your business. Ultimately, the cloud deployment solution will depend on the needs of your organization. Here we help you understand the advantages and disadvantages of each method. Allowing you to compare the private vs public vs hybrid cloud delivery models, and help you choose the right deployment method for your business.

On this page:
- Understanding the Cloud and the deployment models
- Difference between private cloud and public cloud
- Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud – What are the benefits?
- Benefits of Public Cloud
- Benefits of Private Cloud
- Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Private Cloud vs Public Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: Which Cloud type is right for your business?
Understanding the Cloud and the deployment models
What is the Cloud exactly? The term describes a collection of technologies and solutions which provide access, via the Internet, to remotely hosted computing services, hosted in data centres. The components that constitute these computing services, or cloud infrastructure, include storage, hardware, network, and virtualization. Read also: What is cloud computing? So, where do private cloud and public cloud fit in? These terms refer to the manner the remote services are provisioned by the customer – whether that customer is an organization or end-user. There are three predominant ways that cloud services are provisioned:
- Public Cloud – delivered via the Internet and shared across organizations
- Private Cloud – cloud computing that is dedicated solely to your organization
- Hybrid Cloud – any environment that uses a mix of public and private clouds
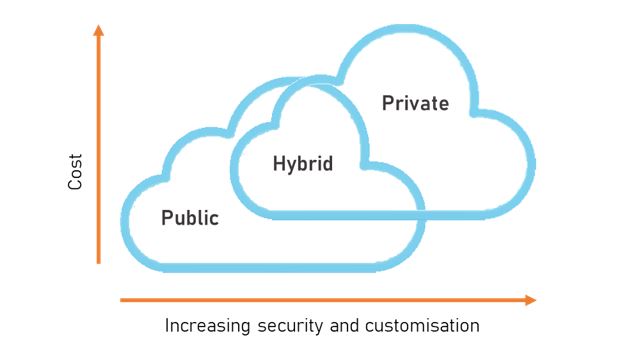
Though each of these modes of deployment has its own value proposition, they can broadly be summarized as presented in the below diagram:
The benefits of cloud computing are significant. For example, by leveraging the Cloud, organizations can:
- Reduce complexity – Effectively release the responsibilities (and overheads) associated with managing and maintaining an in-house IT infrastructure
- Transfer CapEx to OpEx – Transfer capital expenditure to operating expenditure, therebymoving to a subscription model, allowing improved fiscal planning.
- Become more agile and scalable – Introduce an ability within the organization to quickly increase (or decrease) computing services as business needs develop whether that be more for an increase, or decrease, in sales, employees, or regulation.
From driving significant cost savings to improving operations, cloud computing solutions do it all, whilst providing access to the data from anywhere for users.

Difference between private cloud and public cloud
When identifying the most suitable solution for your business, it can be difficult evaluating private cloud vs public cloud. Some of the key questions asked are:
- What are the advantages and disadvantages between private cloud vs public cloud?
- What is the best cloud solution out there?
- Why should a particular solution be chosen?
Deciding on public, private, and hybrid cloud solutions will rest on several factors, business needs, and limitations. To get started, let’s understand the differences between private cloud vs public cloud.
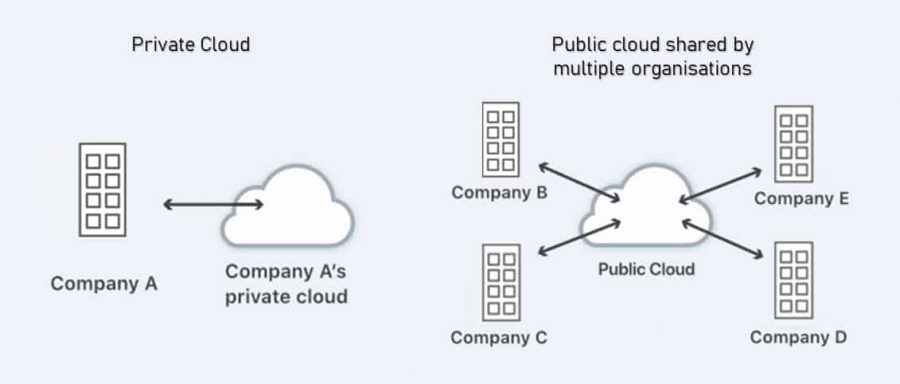
What is Private Cloud?
A mode of deployment where the cloud computing resources are used and operated exclusively by a single organization. Cloud services are delivered through a private network. In the private cloud model, the infrastructure is physically located either onsite, at an organization’s datacentre, or hosted by a third-party provider.
What is Public Cloud?
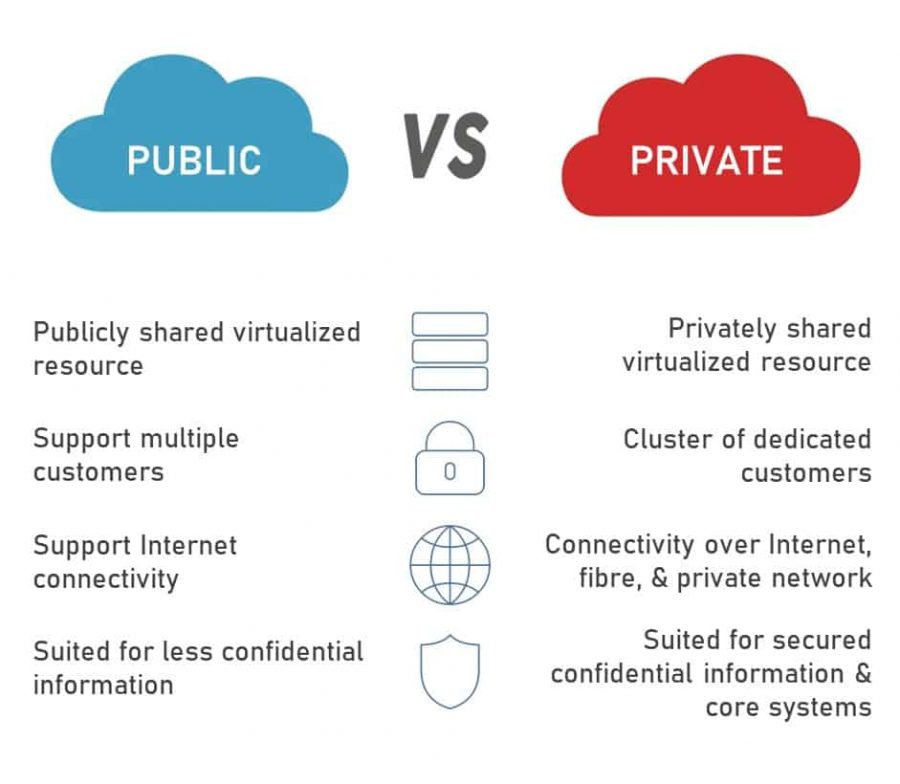
By contrast, in a public cloud model, the computing resources are delivered and accessed through the Internet. The third-party service provider owns and supports all the underlying infrastructure, including all hardware, software, and network bandwidth. You share the hardware, network and storage devices with other organizations which have subscribed to the same cloud service provider.
The public cloud may be considered like renting an apartment in an apartment building. But whilst your apartment itself is secure, there are, for example, shared areas such as the lobby, stairwell. The landlord or building supervisor handles maintenance for the building. In contrast, a private cloud is more akin to renting a house of a similar size to the apartment building. The house offers greater privacy and security, since only you have access to it. However, it is also typically more expensive to rent. A third-party cloud provider can host a private cloud for a business, or the business may choose to host, manage and maintain the private cloud itself, onsite.
What is multitenancy?
Multitenancy is when several cloud provider customers use the same physical server. A single physical server may store the data from two different customers, or the same server could be running two different applications.
Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud – What are the benefits?
If you are struggling to decide which to choose between public vs. private cloud, a third option is a hybrid cloud, which allows you to run public cloud services using private cloud infrastructure. When considering private versus public, or even vs hybrid cloud, it is worth bearing in mind that one is not better than the other. Nonetheless, they are different. While public cloud offers greater scalability and significantly lower upfront costs, private cloud generally offers a greater degree of control and lower ongoing costs.
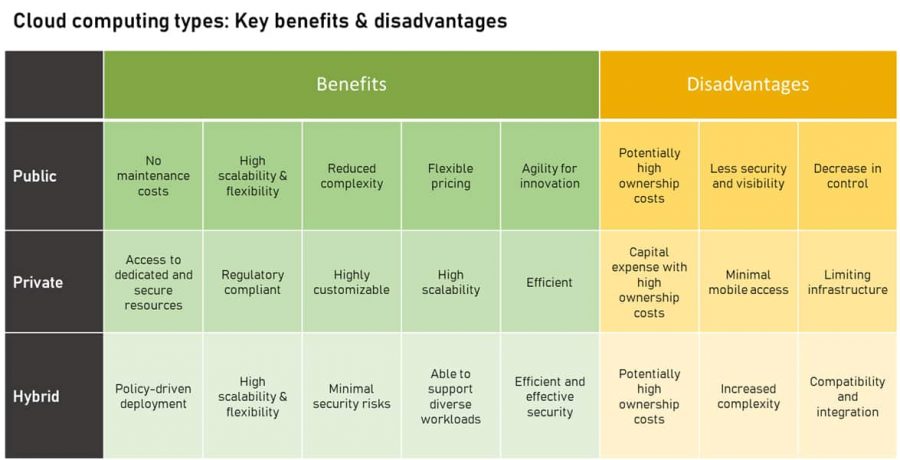
Below we look at each of the modes of deployment in detail, focusing on the advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits of Public Cloud
Public cloud services are delivered via the Internet. Based on the level of use of cloud resources, the cost of cloud computing services offered using the public cloud model can be free, subscription-based, freemium, or paid. In a public cloud model, the hardware, network and storage devices, are shared amongst several tenants. This is commonly known as multi-tenant. These computing resources are managed and maintained by the cloud service vendor. A wide range of services and resources are offered using the public cloud model. These range from the popular, such as email, apps, and storage, to more complex, such as OS platforms along with infrastructure environments. The public cloud deployment model is widespread, particularly, amongst startups, and small and medium businesses, due to its vast choice of solutions and computing resources.
Advantages:
- Low entry costs – Little or no upfront investment is one of the greatest advantages of a public cloud, particular for startups and small businesses. Public clouds are either free or very cost-efficient.
- Highly scalable and flexible – Public clouds come with the flexibility to scale for unpredictable workload demands.
- Fewer complications and knowledge requirements – As the infrastructure is maintained and managed by the cloud provider, the complexities, and the need for in-house IT expertise decreases.
- Flexible pricing – Based on the various Service Level Agreements (SLAs), the pricing options for the public Cloud have a flexible approach.
- Offers cost agility – Due to the “subscription” type method that the public cloud offers, businesses can focus on investing more capital into innovative projects while retaining the ability to grow quickly when necessary.
Disadvantages:
- High ownership cost – Deploying public cloud on a large-scale, may result in a higher overall total cost of ownership (TCO). In particular, this trend is seen with medium and large enterprises.
- Decreased security – From security and critical IT workload points of view, sharing computing resources between multiple tenants in the public cloud, may not be the most appropriate solution.
- Minimal control – Entities needing to meet stringent compliance requirements, such as HIPAA, may experience have difficulty and complexity in maintaining a public cloud environment due to the decrease in visibility and control over the infrastructure.
Public cloud is ideal for:
- Application hosting and on-demand hosting for applications
- Data storage and archiving
- Hosting of large applications where an auto-scaling environment necessary
- Mission-critical web tiers
- Where computing infrastructure is needed to support a large number of customers
- Organizations which are collaborating on projects spanning multiple separate entities. For example, research institutions and NGOs.
Benefits of Private Cloud
The key difference with private cloud vs. other deployment models is that a private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, with the cloud resources either located on-premises or hosted off-site with a third-party vendor. A private cloud’s computing resources are delivered, in isolation, via a secure and confidential private network. Furthermore, private clouds a highly customizable, being able to be tailored to the businesses precise needs, while also meeting critical security requirements. Finally, private clouds offer greater visibility and control over the infrastructure, helping businesses maintain compliance-sensitive IT infrastructures without affecting the performance.
Advantages:
- Dedicated and secure environment – A private cloud offers a dedicated and secure environment. Opting for private cloud allows organizations to maintain and process data on their hardware and software.
- Regulation compliant – By structuring their private cloud deployment to work in compliance with strict regulations, specific compliance requirements can be met and managed.
- Scalable and effective – Without compromising security, private cloud can meet any unforeseen organizational requirements.
- Flexible approach – Opting for a private cloud deployment will provide your organization with an abundance of options. As a consequence, this provides flexibility in decision making while retaining the use of advanced technologies and services.
Disadvantages:
- Limited access for mobile users – Private cloud deployments requiring the highest level of cloud security, may cause difficulty for mobile users needing access to the private cloud.
- Inability to scale – Private clouds deployed on-premise, may be limited by the space available onsite. Any unforeseen demands may be unable to be met due to a limited ability to scale on-premise computing resources.
Private Cloud is ideal for:
- High-performance access to file-system
- Hosting where high data privacy, security, latency are highly regulated
- Hosting business-critical data and applications
- Organizations which can support the expense associated with running next-generation cloud datacentre
- Organizations that need advanced configurations, adaptability and flexibility
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
When comparing hybrid vs. private vs. public clouds, most organizations orientate towards a hybrid cloud deployment. Essentially, this type of cloud deployment is a blend of both the public and private cloud solutions. A hybrid cloud solution works by allowing apps and data workloads to share the resources between private and public cloud solutions. However, the level of hybridization, or sharing of resources, will be unique to each organization and their particular needs, objectives and future growth plans.
Advantages:
- Scalable public cloud environment with robust data security – Hybrid cloud solutions allow for the scaling of a public cloud environment without any compromise on security, keeping sensitive data safe from any cybersecurity risks, improving security posture.
- Extreme reliability – By distributing services across a range of public to private cloud data centres, hybrid cloud solutions are far more reliable vs any alternative cloud deployment solution.
- Cost-effective technology options – By allowing the selection of varying degrees of private and public cloud infrastructures and services, hybrid cloud allow the spreading of workloads across the inexpensive public cloud, to minimize cost, while continuing to leverage the benefits of private cloud technology.
Disadvantages:
- Need for strong integration and compatibility – Hybrid cloud resources typically span several locations and categories. Consequently, the need for compatibility and integration will manifest at some point. Incompatibility issues and unsuccessful integrations can be a limiting factor, primarily due to the lack of direct control over the public cloud infrastructure.
- Added complexity – Since a hybrid cloud is a blend of private and public cloud solutions, inevitably, at some point, your are likely to experience additional infrastructure complications.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud: Which Cloud type is right for your business?
When it comes to private cloud vs public cloud, choosing a mode for cloud deployment is rarely an either/or situation. This is especially true for SMBs, who tend to leverage all three types of cloud solutions to maximize scalability and flexibility to support future growth plans. Though your business is likely already using the Cloud, for SMBs, it is worth developing a cloud strategy to optimize your use of each cloud deployment model. A good starting point is by defining the needs of your various workloads and then prioritizing these workloads based on the advantages and disadvantages of each cloud model presented above.

