SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Which cloud service is right for your business?
Cloud services have become increasingly crucial for all organizations, with at least one type of cloud service being used by most businesses. However, when comparing cloud services, the most pressing question for organizations is, what type of cloud service to use – SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS?
While each cloud service offers its own benefits, it is crucial for organizations to understand the key differences between these three, to understand and help determine which is most appropriate for your business.
Below we present everything you need to know about Saas, PaaS, and IaaS.
On this page:
Saas vs PaaS vs IaaS: The key differences
Cloud computing is the provision of remote computing resources via the internet. The remote resources are accessed via a web browser and can range from applications, to databases to the ability to create and manage remote servers.
Cloud technologies offer many benefits for business and organisations of all sizes and in all sectors. Some of the benefits organizations can realise from using cloud computing are:
- Reduction in capital expenditure on IT hardware and infrastructure
- Ability to quickly scale IT capability to match business growth
- Flexibility for business demands and operations
- Advanced and centralized storage facility to keep the data stored securely
Read also: Understanding Cloud Computing – What is cloud computing
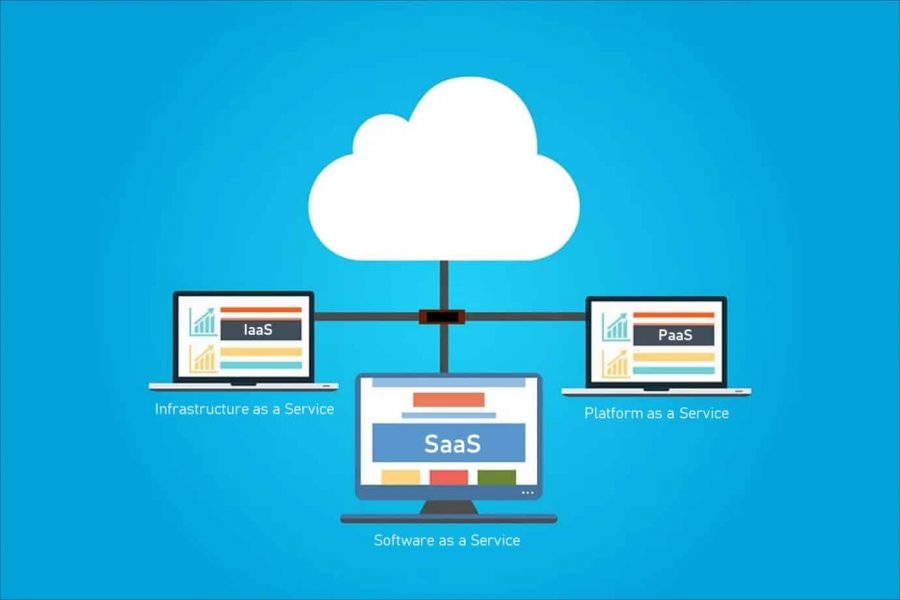
When commencing their cloud journey, most organizations will consider three types of cloud service models to compare: SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS. Each of these models describes the distribution of cloud services.
Since each of these models offers their own value proposition and benefits, it is advisable to understand the differences between SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS to select the right choice for your organization:
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – A model where software is hosted by a service provider and accessed over the internet or network.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) – Provides an environment, platform and tools for developers to build applications and services. The environment, platform and tools are hosted by a vendor or service provider and accessed via the internet.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Offers remote access, via the internet, to computing resources such as storage and networking, typically in a virtualized environment.
As with any technology-related decision, you should evaluate the pros and cons of cloud computing, to understand which cloud model is the right fit for your enterprise. When considering SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS, the the advantages and disadvantages of each licensing and delivery cloud service model needs to be clearly understood.
Related: Private Cloud vs Public Cloud: Which Cloud Computing model is best for your business
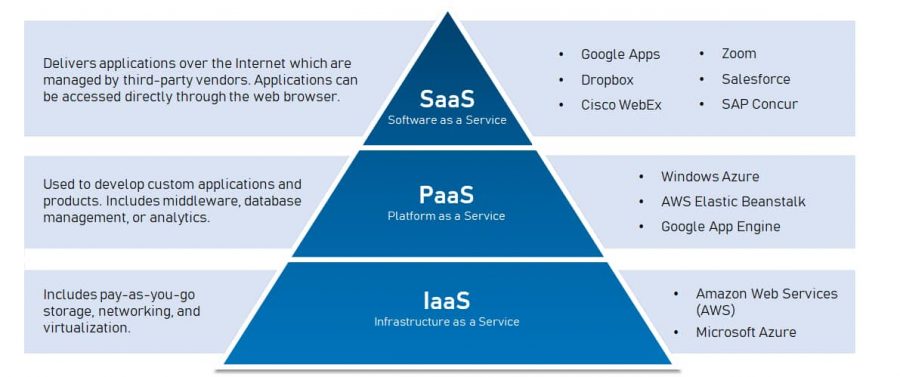
Generally, the SaaS model is the most popular cloud service, offered typically in a subscription form via the Internet. Online accounting software and online video conferencing software are good examples of the SaaS model.
PaaS, on the other hand, is more focused on developers, providing a more niche appeal, by offering the ability to quickly set-up and scale environments and platforms for the purposes of software development, testing and deployment. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers the most customization and control for an organization, providing access to “barebones” resources such as storage, processing power, memory and networking via the Internet.
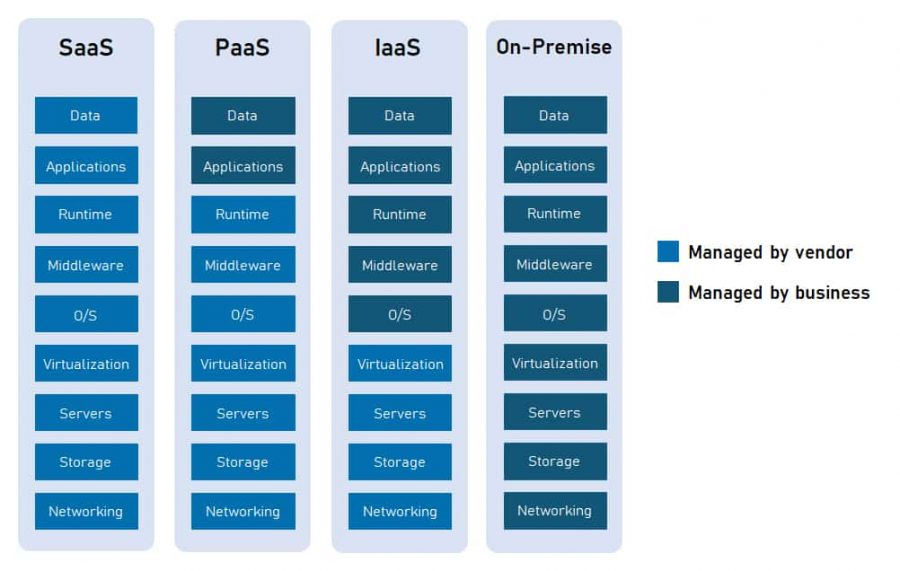
SaaS offers the least complexity for organizations, without the need for businesses to manage the infrastructure. However, this comes at a cost – SaaS also offers the least customization. In contrast, the opposite is true for IaaS. Fortunately, depending on the requirements, an organization can use one service model or all three.
For decision-makers comparing SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS, presented below are further details for each of these models, including their respective pros and cons, and examples.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
A comparison of SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS, quickly reveals software as a Service (SaaS) is the most popular type of cloud service model currently in use by businesses today. SaaS delivers applications via the Internet which are managed and supported by the vendor, and are run directly through the web browser, without the need to download and install any files.
SaaS applications are extremely easy to use and manage. SaaS is offered on a subscription model, typically on a cost per user per month basis. This model allows easy deployment, scalability, and versatility allowing fast set-up on several devices, and the ability to scale very quickly.
Organizations simply manage user access to the SaaS application, with the vendor responsible for the underlying infrastructure and support. Cloud accounting software, cloud video conferencing software as well as several popular productivity tools are examples of Software as a Service (SaaS).
SaaS is used by a wide range of businesses, from start-ups to large enterprises, offering low capital expenditure requirements and low administrative overheads.
Advantages of SaaS:
- Available through common web browsers
- Usually available on desktop and mobile devices
- No requirement for installation
- Reduction in administrative overheads, you only need manage user access
- Improved usability – Employees can use the software without the need to download any files. Employees simply need to sign in to use the software
Disadvantages of SaaS:
- No control over the infrastructure which the software operates on. In case of an outage, business productivity can be impacted

Platform as a Service (PaaS)
The best wasy is to describe Platform as a Service (PaaS), is to think of it as an environment to develop applications and products. This environment allows developers to build and test custom applications without needing to invest in, and manage, the underlying infrastructure.
Using PaaS, developers can quickly and easily deploy large applications with little capital investment in related infrastructure. Instead, they can establish and emulate various environments to build and test their applications, emulating combinations of servers, databases, operating systems, and more.
PaaS is provides a robust platform for developer and software development businesses which regularly develop and manage any kind of application, and may have developers spread over a large geographical area. Heroku and Google App Engine are some examples of PaaS.
Advantages of PaaS:
- Provides a significant level of control over the platform software and the applications built with the platform
- Often supports multiple programming languages, providing developers the opportunity to work on several different projects.
Disadvantages of PaaS:
- In case of a service outage, you will not be able to access the software, thereby impacting productivity
- Unforseen charges – particularly as the service grows
- Fundemental coding knowledge would help businesses get the most value out of PaaS

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. The computing resources include storage, networking, processing power, memory and virtualization.
The actual physical infrastructure will be provided and managed by the cloud provider. As business, you, the customer, will be responsible for nearly everything else, including the installation and setup of the operating system, virtual machines (VM), and any other applications that may be required.
With IaaS, organizations do not have to deploy, configure, and maintain the physical equipment that your business applications need, instead deploying the same specification of infrastructure in an IaaS model. This approach significantly reduces the overheads and capital investments traditionally associated with IT infrastructure.
Since the IaaS costs are driven by the consumption of the services, you retain flexibility and scalability. Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsfoft Azure are both examples of IaaS.
Advantages of IaaS:
- Significantly lower or no capital expenditure for hardware infrastructure, such as servers, storage, networking resources.
- Improved scalability – on demand access to “raw” computing resources on a pay-as-you-use basis, allowing you to scale as the business demands.
Disadvantages of IaaS:
- Higher total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Need to retain some in-house or specialist knowledge to maximise the potential of the IaaS computing resources.
- Added complexity and management – While easily scalable, unnecessary workloads may continue use computing resources, resulting in unforseen costs.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Which model should you select?
Each organization will have differing requirements, and selecting the right cloud computing service model will depend upon ensuring that your needs of your business are met. The following points will provide some guidance for organizations looking to compare SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS:
- For organizations which need out-of-the-box services like CRM, email, collaboration tools, then out of SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS, SaaS offers the best choice. SaaS offers a ready-to-use service which can business needs easily.
- Businesses seeking to build software products, either for employees or customers, the provision of an development environment, platform and tools offered by PaaS provides a good fit.
- IaaS make the most sense for companies who need a completely flexible workplace, with a high degree of customization, particularly the need to regularly provision virtual machines.

