Internet Keeps Dropping? Here’s What to Do…

When your internet keep disconnecting and reconnecting, it impacts productivity and can interrupt important tasks.
Whether for production line connectivity, remote healthcare applications or office worker productivity, downtime due to frequent internet drops can cost your business time and money.
Frequent interruptions are usually a sign of problems, such as a bad Wi-Fi signal, old hardware, or an ISP-related issue.
Learning what causes these interruptions lets you troubleshoot and resolve these disruptions so you can stick with an uninterrupted connection.
On this page:
- Internet Keeps Dropping? Quick Tips
- Why Does My Internet Keep Dropping?
- Internet keeps disconnecting and reconnecting? Here’s 5 Quick Fixes
- Advanced Troubleshooting for Internet Connection Drops
- Long-Term Solutions for Stable Internet
- Internet Keeps Disconnecting? Here’s Expert Tips for Maintaining your Connection
- Technical Factors Causing Dropouts
- Seeking professional advice if your Internet keeps disconnecting
- Internet Keeps Dropping: Frequently Asked Questions
Internet Keeps Dropping? Quick Tips
- If your internet keeps dropping regularly, this can usually be attributed to hardware malfunctions, network overload, or obsolete devices.
- Make sure your modem and router are well-placed. Check in on your modem and router to be sure they’re working correctly and positioned for best signal strength.
- When your router or modem firmware is faulty, corrupted or out of date, it can cause ongoing connection problems. Keep your devices updated to maintain performance and security.
- Keep an eye out for internet service provider (ISP) outages, and reach out to your ISP support if issues continue.
- Try to limit active devices. Overloading your network with too many connected devices that consume a lot of bandwidth can impact performance.
- Reduce physical barriers, and prevent interference from other electronics. Physical barriers, such as walls and furniture, wireless interference, and incorrect placement of a router can all hamper Wi-Fi.
- For chronic disconnects, more technical troubleshooting like resetting network settings, updating wireless drivers, or changing router settings may be necessary. Keep a log of what you’ve tried and consult an expert if issues persist.
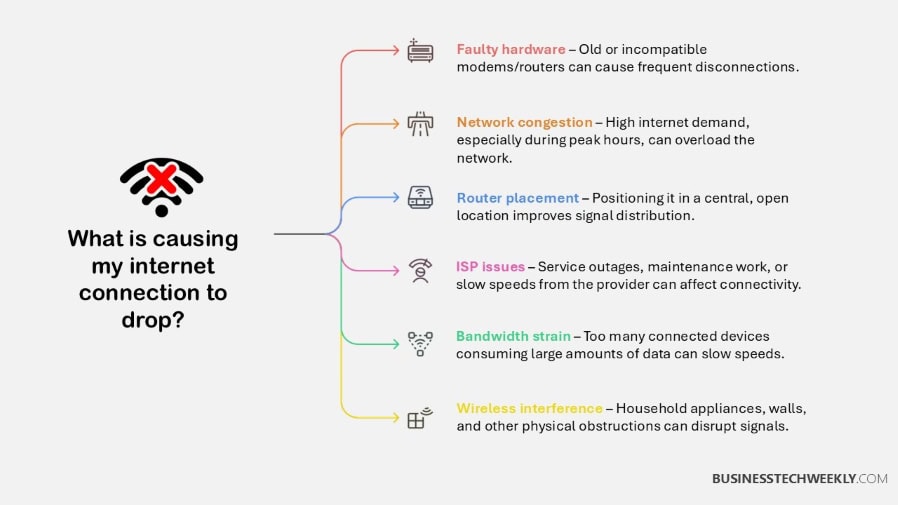
Why Does My Internet Keep Dropping?
When the frustrating reality of intermittent internet disconnections interrupts your webinar on Zoom, identifying the cause of your internet problems is essential.
Once you pinpoint the issue, you can take steps to enhance your home network and ensure a stable internet access for a more reliable internet experience.
A quick fix may be as straightforward as replacing you existing equipment with a more modern, and technologically advanced wireless cable modem combo device.
Let’s take a look at the biggest causes of dropped connections and what they do to your network’s performance.
1. Common Causes of Dropped Connections
If your internet keeps dropping interrupting your webinar on Zoom, identifying the cause of your internet problems is essential.
Recurring losses of connectivity are usually caused by faulty gear or misconfigurations. Broken wires or other faulty connections between your modem and your ISP service can cause drops.
Most home connections have three types of cables:
- Ethernet cable – If your modem and router are not a package, you will need this cable. It also connects the router to your computer to enjoy a direct signal.
- Coaxial cable – This cable connects a modem to the cable network in the home.
- Phone cable – Your modem/router combo or modem connects to the DSL internet line with this cable.
Annoyingly, old hardware can’t process the high-speed data needed today causing your internet to keep dropping.
Network congestion at peak times is another frequent culprit, as to why your internet keep disconnecting and reconnecting frequently.
Router placement plays a key role—placing it in a central, open location ensures better signal distribution throughout your space.
RELATED: Securing your wireless network
2. Router and Modem Problems
Faulty routers are the number one cause when it comes to why your internet keeps dropping.
Faulty routers are the number one cause when it comes to connection drops. Because as they get older, internal components start running the risk of major failure, causing you to continually disconnect.
For performance, modem compatibility with your ISP’s network is important. Older models might not support anything above 25 Mbps, for example, or newer, more efficient protocols like DOCSIS 3.1.
Router firmware is another aspect to consider. Most people don’t think to check for a firmware update, but outdated firmware is a major cause of internet keep disconnecting and reconnecting.
Physical damage, like overheating or broken ports, can lead to issues with connection.
3. ISP-Related Interruption Issues
Unsurprisingly, your ISP can be the cause if your internet keeps dropping. Outages or maintenance work on their end can cause a temporary drop in your connection.
Symptoms such as slow or degraded speeds, or enough people in your community having trouble that they’re reporting to the FCC, usually indicate an ISP cause for internet keep disconnecting and reconnecting.
A simple trip to your provider’s service status page should allow you to quickly determine whether these unexpected disruptions are caused by outside factors.
4. Device Overload and Bandwidth Strain
Bandwidth strain is an unfortunate reality when too many devices connect to the same network. Things like streaming in 4K or playing video games online use up a lot of data, which means less bandwidth for everything else.
Limiting the number of simultaneously connected devices can help prevent internet keep disconnecting and reconnecting.
5. Signal Obstruction and Wireless Interference
Physical barriers, like thick walls and big metal objects, can contribute to the cause if your internet keeps dropping. Household appliances like microwaves and cordless phones can lead to interference.
This is especially the case when they are sharing the same 2.4 GHz frequency. Utilizing the 5 GHz band for compatible devices and reducing obstructions in your home can help improve signal strength.
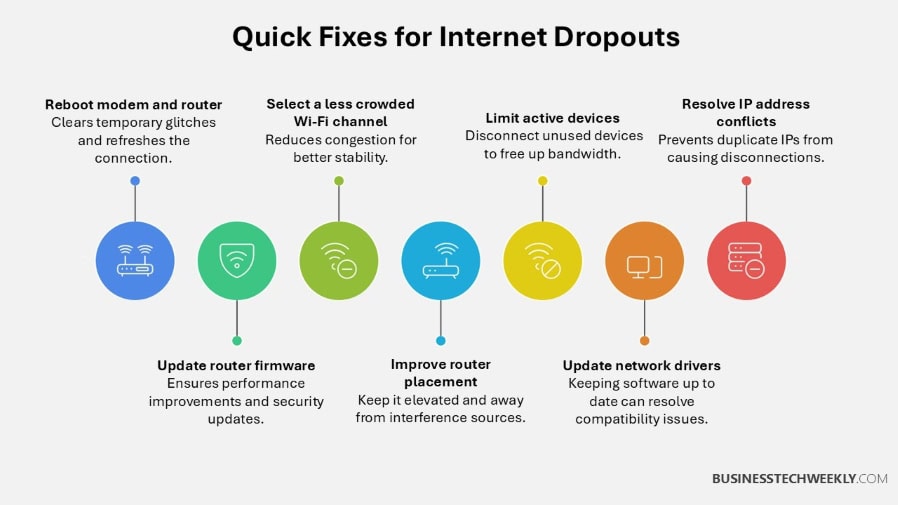
Internet keeps disconnecting and reconnecting? Here’s 5 Quick Fixes
When your internet keeps dropping, it kills productivity and can impact emergency response or other essential work.
Addressing these internet connectivity problems in a timely and efficient manner will avoid repeated interruptions.
Here are quick fixes you can take to stabilize your connection and maintain a reliable internet experience.
1. Reboot Your Modem and Router
Rebooting clears out any temporary glitches or other major issues you might have that are interfering with your connection.
Begin by completely power cycling your modem and router. Wait 5 to 10 seconds before powering them on again.
This step allows the devices to reset their internal memory, eliminating small glitches. When done on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, these regular reboots keep overall connectivity stable.
Rebooting gives your devices the opportunity to re-negotiate with your ISP to reconnect with a clean slate and a lower likelihood of experiencing dropouts.
What is the Best Ethernet Cable?
You may have purchased Cat-5 Ethernet cables a few years ago, but as time passes, it’s likely time to consider changing to a more contemporary choice.
Cat 8 cables are also waterproof, anti-corrosive, and made of a more robust PVC material, making them ideal for indoor or outdoor applications. It’s an excellent choice for business or personal cable management, and it may also result in a considerable performance boost.
- 🔌【Ultra Internet speed】Cat 8 ethernet cable...
- 🔌【RJ45 Connectors & Wide Compatibility】With two...
- 🔌【Durable & Weatherproof & UV Resistant】Cat8 lan...
2. Refresh Router Software
Outdated firmware can negatively affect performance and is a common cause of internet keep disconnecting and reconnecting.
Log into your router’s admin settings—typically accessible through a browser using the router’s IP address—to check for available updates.
Do this by downloading and installing the latest firmware available from the manufacturer.
Regularly updated software means bug fixes and smoother functionality, meaning a more reliable connection and better overall security.
Related: Boost your Wi Fi
Here are the steps to easily install the latest network drivers:
- Open the Start menu and look for Device Manager.
- In the Device Manager, you will find Network Adapters.
- Click on the arrow next to the option to see a list of drivers.
- Search for the appropriate drivers on the web to find their latest updates.
When you look for drivers, always download them from the official website and go through the details carefully to avoid downloading any additional programs.
Once downloaded, run the file and follow the process. It is best to restart the system after installing the drivers.
Then, you can run a test to see if the problem is fixed.
3. Select a Less Crowded Wi-Fi Channel
Wi-Fi congestion can contribute to a poor, intermittent signal.
Alternatively, use a Wi-Fi channel analyzer, such as Wi-Fi Analyzer or inSSIDer, to find the least crowded channels.
Change to a less congested channel through your router’s administrator dashboard to get a better signal.
Using the 5 GHz band, if your devices support it, cuts out interference even more and improves speed for devices that are close by.
4. Improve Router Proximity
If your router is too far from your devices, you may notice your internet keeps disconnecting and reconnecting due to weak signals
Position your router in a central location and raise it above ground level, ideally on a shelf.
Don’t put it by outside walls or appliances such as microwaves that may disrupt the connection.
It will help you find the best location for coverage if you test various locations.
5. Reduce Number of Active Devices
Disconnect devices you’re not using—even printers or TVs—to reduce network output and improve your connection.
Run resource-intensive processes such as server backups or application updates during off-peak hours.
Restricting the number of active connections helps make sure important applications, such as video calls and telehealth, function without interruption.
6. Refresh Network Card Software
Check for outdated network drivers. Disconnection issues might stem from having old network drivers.
Manually update your device’s network adapter drivers using Device Manager.
Frequent releases make sure that you’re always compatible with the latest network and transportation protocols.
7. Resolve IP Address Conflicts
Especially when behind a NAT, IP conflicts can cause connections to drop unexpectedly.
Review your change network settings so that you are not running into duplicate IPs.
Either assign unique IP addresses on your devices or allow the DHCP server/ router to assign them automatically.
By facilitating resolution of these conflicts, more certainty and stability is provided to the network.
8. Switch to Ethernet
An unreliable Wi-Fi connection is one of the biggest reasons you can experience internet dropping while watching videos, streaming, or playing games.
Though you can opt for access points, repeaters, and other Wi-Fi aids, a Wi-Fi can never be relied upon for consistent performance.
It always has variables and more latency as compared to traditional cable connections. If you cannot afford to deal with the occasional internet drops, using an Ethernet cable is the best solution.
A Wi-Fi can suffer from a variety of problems and will never be as reliable as plugging the Ethernet cable into the device and connecting it to the router.
These cables are available in lengths up to 100 meters for affordable prices so it is easy to switch to this mode of connection.
- VPN Server: Archer AX21 Supports both Open VPN Server...
- Certified for Humans: Smart home made easy for...
- Dual-Band WiFi 6 Internet Router: Wi-Fi 6(802.11ax)...
Advanced Troubleshooting for Internet Connection Drops
When persistent internet dropouts keep your operation in frustrating stasis, affecting productivity and morale, it’s no laughing matter.
Meeting these hurdles takes an intentional effort, one that blends expertise in the technology with real-world answers.
Here are steps to guide you in troubleshooting internet connectivity problems and diagnosing common connection issues.
1. Update Wireless Adapter Drivers
Installing obsolete wireless adapter drivers will further restrict network performance, frequently causing your internet to keep dropping.
Begin by verifying your device driver version using Device Manager (on Windows) or System Preferences (on macOS).
Manufacturers are constantly updating their products to squash bugs or make a product work better with other popular products.
To avoid being stuck with an outdated or unstable driver, always download the latest drivers directly from the manufacturer’s website.
Keeping drivers and infrastructure in good working order with proactive maintenance means fewer problems from the get-go and less chance of future headaches.

2. Configure Power Saving Settings
Often the first whodunit, laptop and mobile power-saving modes can cause disconnects by preventing all network activity.
For Windows users, go into Device Manager, find your wireless adapter, go to properties, and then disable any power-saving features.
On macOS, these types of settings can be changed in the Energy Saver preferences as well.
Finding the right balance between energy efficiency and reliable connectivity is key, and disabling these modes typically provides a more stable connection.
3. Fine-Tune Router Configuration
Proper router settings are very important for keeping a good, stable connection. Change the channel selection to avoid interference.
Turn on Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize bandwidth, and ensure that WPA3 encryption is enabled for added protection.
Open your router’s configuration page by entering its IP address, usually found on the router’s device information label.
Weekly router restarts and occasional firmware updates keep things running at top speed.
4. Reset Network Settings
Resetting network settings or network state can help remove lingering misconfigurations and errors.
On Windows, you can use the “Network Reset” feature found in Settings → Network & internet → Network Reset.
On macOS, delete and re-add your Wi-Fi connection.
Make sure you record customized settings in advance like static IPs or DNS preferences so you can reconfigure them after the reset.
5. Hardware Diagnosis and Replacement
Faulty hardware, a silent killer of persistent problems, can be a significant issue.
Hardware that is considered requisite for the application should be examined.
Examine the cables for fraying or other issues that could affect performance.
Try the connections with a backup modem or router, and consider replacing devices older than five years.
For homes that require a high-bandwidth environment, tri-band routers or tri-band mesh systems offer increased performance.
6. Confirm Service Outages with ISP
Check for known outages on your internet provider‘s website, social media, or customer service number.
Being aware of these potential internet issues can save you significant troubleshooting time, especially during network disruptions that affect larger areas.
7. Boost Wi-Fi Signal Coverage
Fix coverage by moving your router away from walls or appliances.
Wi-Fi extenders, or upgrading to dual-band routers (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) reduce interference and enhance stability.
Devices that require legacy compatibility will see an improvement when MLO is disabled and frequency bands are separated.
Long-Term Solutions for Stable Internet
Having an effective, stable, internet connection is essential to supporting frequent use whether at home or in the workplace.
While some unexpected disruptions will always occur, smart investments and proactive strategies can go a long way toward minimizing connectivity loss in the long term.
Read on to learn about long-term solutions that can get you a more stable, efficient network.
Upgrade to a Modern Router
All these reasons make investing in a Wi-Fi 6 router a worthwhile investment with easily noticeable benefits like increased speeds, heightened security and wider coverage.
This enables dozens of devices to access the internet simultaneously without any delay. Look for support for Wi-Fi 6, which increases performance in dense environments.
For instance, households with multiple gamers or remote workers may need to invest in advanced routers optimized for heavy use.
It’s equally important to make sure they are fully compatible with your ISP’s standards to prevent bottlenecking speeds.
A general guideline would be to change out routers every 5-7 years at a minimum in order to stay ahead of innovation.
Consider Fiber Optic Internet
Communities with fiber optic internet enjoy much faster and more reliable connectivity than DSL or cable. It sometimes is over 1Gbps.
This makes it ideal for homes or offices with heavy data usage, such as video calls or streaming.
To find out what is available, engage with local internet service providers (ISPs) or use online checker tools.
Providers such as Infinium offer very competitive fiber plans, but watch out for contract stipulations, including a 24-month commitment.
If fiber isn’t an option, ask about hybrid solutions for faster speeds.
Prioritize Network Traffic
Set up QoS Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize bandwidth usage.
Give priority to essential activities like video conferencing and cloud backup so they run without a hitch.
Consider, for instance, applying QoS to prioritize productivity applications over less critical bandwidth during work hours.
Fortunately, most modern routers come with intuitive dashboards to set priority bandwidth through QoS protocols.
For more congested networks, this guarantees better performance, especially for more congested or shared networks.
Explore Dual-Band or Tri-Band Routers
Routers with dual or tri-band capabilities are better equipped to manage high-demand households by distributing traffic across various frequency bands. Dual-band routers offer both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz channels.
Tri-band routers go a step further and add an additional 5GHz band, making these perfect for larger homes. These choices are smart ways to help alleviate congestion now and future-proof your network to handle escalating demands.
Ethernet Over Powerline or Coax
Ethernet over powerline adapters use your home’s electrical wiring to deliver ethernet connections, avoiding Wi-Fi range issues.
This arrangement is convenient when needing to reach difficult spaces such as basements.
In a pretty straightforward kit, adapters plug into the wall sockets next to your router and devices.
This approach provides a level of stability that can rival even hard-wired Ethernet connections.
Proactive Network Monitoring
Advanced monitoring tools—such as NetSpot, GlassWire, and others—allow users to actively monitor internet speeds and detect connectivity issues before they become major problems.
Periodic evaluations help you make sure your network is performing at its best.
When performance becomes unacceptable, for instance, monitoring can confirm the presence of throttling from your ISP and objectively prove its impact.
Address issues early by rebooting equipment monthly and inspecting cables for hidden damage to maintain a healthy network.
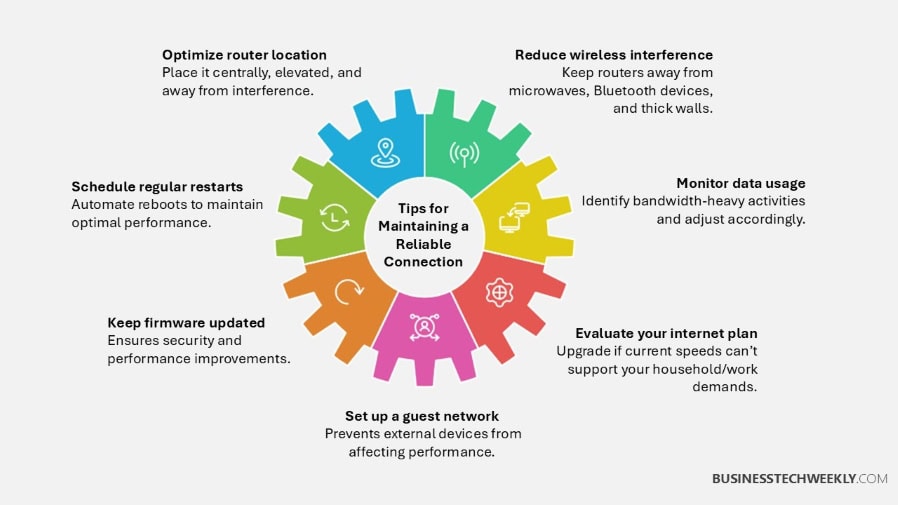
Internet Keeps Disconnecting? Here’s Expert Tips for Maintaining your Connection
Having a reliable internet connection is crucial for everyday life and work, especially to avoid internet connectivity problems.
Prioritize proactive strategies and perform routine maintenance on your network hardware to improve your internet speed and reliability. Tailor to your unique context to maximize impact even more.
1. Optimize Router Location
Your router is essentially a beacon of your internet connection, so placing it wisely can come a long way.
Place your router in a central location, high off the ground, and away from walls or metal surfaces.
For example, setting it on a shelf in a common area increases its usage.
Remove impediments such as heavy household furniture or appliances, which can block signals.
Try out a few locations to find the ideal combination of connective speed and stability for your home or workplace.
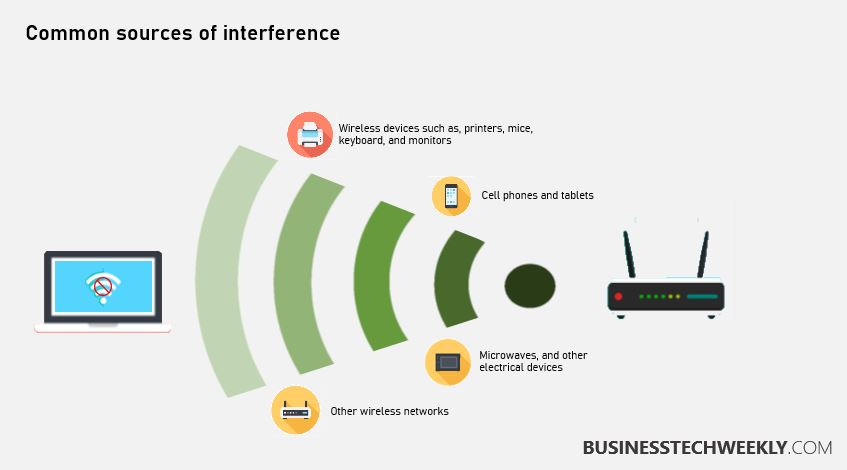
2. Minimize Interference Sources
Wireless interference can degrade your connection. Common sources include microwaves and cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and thick walls or floors.
To find interference, use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to help you identify issues and then switch your router to a less congested channel.
Keeping a clear line of sight between your router and your devices is key in providing stronger signals.
3. Schedule Regular Restarts
Restarting your router and/or modem resets any temporary glitches and helps improve performance.
Configure automatic restarts for updates during off-hours of low-usage times, or take the time to manually restart them every week.
This easy ritual helps you fix everyday connection hiccups while ensuring your network’s health is in check.
4. Track Data Usage Patterns
Monitoring bandwidth helps identify devices or activities consuming excessive data.
Tools such as your router’s dashboard or third-party apps such as Homefire or Kiwi can help you monitor data use.
Knowing your usage patterns helps you determine if you need a higher internet plan or if you need to prioritize bandwidth for more essential activities.
For families, 500Mbps should be more than enough even with five active users.
5. Maintain Up-to-Date Software
Keeping the firmware and other drivers up-to-date helps reduce vulnerabilities and maintain strong performance.
Ensure you keep all routers, modems, and network adapters updated.
Ensuring your connection is robust is crucial.
Updated software is more secure and includes the most recent features and enhancements.
6. Evaluate Internet Plan Needs
Reevaluate your internet plan at least once a year.
Think about how many people are using it, what you watch on what service, how many smart appliances you have, and more.
In this case, upgrading to a faster plan wouldn’t be an option once your needs expand. In order to get the best value, always align your plan with what you really use.
7. Implement Guest Network Access
Setting up a separate guest network adds a layer of security by isolating all the visitor activity from your primary connection.
This helps increase security and ensures that bandwidth won’t be overwhelmed.
Most newer routers have easy guest network setup features that can be set up through your router’s app or online interface.
Technical Factors Causing Dropouts
This constant chance of internet dropouts can be irritating and disruptive, significantly whenever they affect companies.
By learning about some of the basic technical factors at play, you can set yourself up to make a bigger impact.
Connectivity issues are most often caused by a perfect storm of old technology, harsh terrain, and poor network setup.
Understanding and addressing these issues goes beyond simply keeping a trusted connection.
Outdated Firmware and Settings
Keeping router firmware up to date is another common 5G disconnection culprit.
Firmware updates should be a top priority, as they continually address bugs and security issues while implementing new performance enhancements.
Failing to apply manufacturer updates could have your modem or router unable to keep up with today’s high-speed data, resulting in constant dropouts.
To see if updates are available, log into your router’s admin panel through a web browser and look under the router’s firmware section.
The guidance doesn’t stop there — manufacturers frequently have detailed guidance on their websites.
Misconfigurations, like default Wi-Fi channels or enabled power-saving modes, can lead to problems as well.
Regularly adjusting these settings and installing updates will ensure that your network is operating at peak performance.
Physical Obstructions and Interference
Physical barriers such as walls, couches, or metal surfaces reduce a Wi-Fi signal’s reach.
Adding interference from other devices such as Bluetooth audio devices, baby monitors, or a good ol’ microwave oven continues to compound on this problem.
To maximize signal strength, place your router in the most central, elevated location possible, with the fewest number of barriers around it.
Regularly checking your environment will help you maintain a clear signal path, with less interference and better connectivity.
Diagnosing Internal Hardware vs. ISP
When you run into connectivity issues, figuring out if the issue is on your end (your hardware) or your ISP’s end is important to resolve if your internet keeps dropping.
First things first, learn to troubleshoot your connection by examining your modem, router, and cables for wear and tear or loose connections.
Using another device to test the connection or rebooting your equipment can help rule out the source of the problem.
Documenting your observations, such as error messages or specific times of dropouts, provides valuable information when contacting your ISP for resolution.
High Network Traffic and Peak Usage
Peak usage creates congestion, especially in the evening hours, when multiple users are likely online at once.
Implementing strategies such as scheduling bandwidth-heavy tasks during off-peak times or options like upgrading to a higher-speed plan can help reduce the slowdown.
When you understand traffic patterns, you can better plan for usage spikes and use your network efficiently without overloading it.
Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
Quality of Service (QoS) settings on routers allow for prioritizing bandwidth to the most important applications such as video calls or online gaming.
Properly configured QoS improves the overall user experience by prioritizing and allocating performance resources to where they’re needed most.
Consistently monitoring and tweaking your QoS parameters keeps you in harmony with wherever your needs stand today.
Environmental Factors and Weather
Environmental factors, such as extreme weather events or a lack of proper insulation, can affect access to connectivity.
High winds or heavy rain, for instance, can force down cable lines or flood satellite dishes.
Continuously monitoring weather forecasts and allocating resources towards weather-resistant equipment can help reduce external conditions that lead to disruptions.
Seeking professional advice if your Internet keeps disconnecting
Connectivity issues on the internet can be painful at any time, especially when they interrupt essential business operations.
Though many problems are easily solved with some straightforward troubleshooting, there are clear symptoms when you need to call in professionals.
Persistent problems, such as frequent outages, DNS resolution errors, or intermittent drops, may indicate underlying technical challenges requiring professional intervention.
Contacting Your Internet Provider
When your connectivity problems aren’t resolved, contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is often the next logical step.
To make the process smoother, ensure you have the following details ready:
-
Specific account information, like your account number or billing address
-
Specific dates and times when the issues occurred
-
A summary of troubleshooting steps you’ve already attempted
-
Any error messages or unusual network behavior observed
Healthy, strong communication goes a long way when talking to any form of customer service.
Explain symptoms concisely, such as “The connection drops every afternoon between 2 PM and 3 PM,” instead of vague phrases like “It’s not working.
Ask focused questions, such as:
-
Are there known outages in my area?
-
Could my equipment or settings be causing the problem?
-
Are there recommended steps for improving connectivity?
Continually checking in on outstanding questions keeps them honest.
Ask for a case number so you can reference and track the communication for possible further discussion.
Hiring a Qualified Technician
When problems are more serious or complicated, it may take the skill of a trained professional to sort out their causes.
The cost of hiring an IT specialist or network engineer will be well worth it in the time saved and future disruption prevented.
Among others, CompTIA Network+ or CISSP are some of the certifications a professional should have to be able to provide credibility. Finding the right local technician is critical.
Read reviews, check their credentials, and ask for referrals from sources you trust.
Before you hire anyone, get an estimate and projected timeline for the repair work, so you are not caught off guard.
For instance, DNS misconfigurations or long-term compromises typically require advanced capabilities and expertise, thus necessitating outside help.
Clearly Explain the Issue
Clear, direct communication helps move troubleshooting along quickly. Include these details when describing the problem:
-
When the issue started and its frequency
-
Specific symptoms, such as slow speeds or error messages
-
Any temporary fixes that worked
Providing a record of issues, such as maintaining a chronological log of incidents, assists practitioners in diagnosing issues quickly and accurately.
Internet Keeps Dropping: Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my internet keep dropping?
Inability to maintain a stable internet connection might arise from poor signal, equipment obsolescence, or interference from nearby devices.
This could be due to ISP issues or network congestion, leading your internet to keep dropping.
Rule 1— Address your internet problems and hardware issues.
What should I do if my Internet connection keeps disconnecting?
Power cycle your modem and router to improve your internet speed.
Inspect ethernet cables for wear-and-tear and loose cable connections.
If the issue continues, reach out to your internet provider for support with potential internet issues.
What are common technical reasons for my Internet to keep disconnecting and reconnecting?
Technical causes of internet problems could be outdated router firmware, networks that are over capacity, or issues within the customer’s modem/router.
Electrical interference or using older devices that do not comply with current standards can lead to intermittent disconnections.
A little TLC goes a long way; regularly updating and performing maintenance is key for a stable internet connection.
Should I upgrade my router to fix dropouts?
If your router is several years old, it may not support sufficient bandwidth, leading to internet connectivity problems and frequent disconnections.
Upgrading to a modern router can enhance your internet speed and ensure a more reliable internet experience.
How can I maintain a stable internet connection?
To ensure a stable internet access, keep your router in a central location, regularly update its firmware, and use wired connections whenever possible to avoid potential internet issues from network congestion and interference from other devices.
Should I call a professional if my Internet keeps dropping?
If you’ve run through all basic troubleshooting, upgraded your outdated router, and the problem of unstable internet connection still hasn’t improved, call in a professional to diagnose potential internet issues like faulty wiring or ISP problems.
Is it normal for my Internet to keep disconnecting and reconnecting frequently?
No, frequent disconnections and internet connectivity problems are not normal.
Whether it’s due to signal interference, overloaded networks, or faulty hardware, addressing these common issues will significantly enhance your internet speed.
Last update on 2023-05-24 / Price incl. tax, excl. shipping / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API

