LAN vs WAN: What is the difference between a LAN and a WAN?

Today, networking is at the core and backbone of all organizations. WANs and LANs are responsible for driving and facilitating corporate communication and other critical activities. But, what is the difference between a LAN vs a WAN?
Your business can function as effectively, efficiently, securely, and profitably as possible with a well-designed and configured business network. Most companies primarily use two main types of networks – local area networks (LANs) and wide-area networks (WANs).
Here, you can learn the critical components of both networks, comparing LAN vs WAN, and how they may help your organization function more efficiently.
On this page:
Types of Networks
When multiple computers, smartphones, servers, devices, and workstations communicate, they form a network. There are several types of networks used in a business environment:
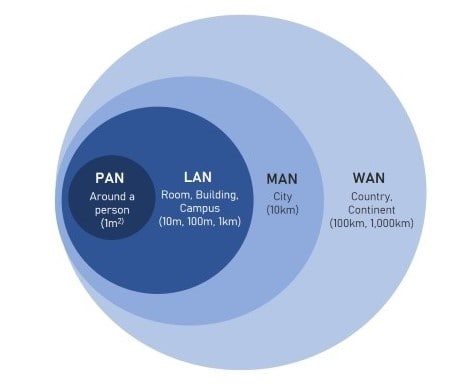
- Personal Area Network (PAN) – A computer network used to connect electronic devices in a single user’s workplace. A PAN connects devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets to one another.
See also: What is a Personal Area Network (PAN)?
- Local Area Network (LAN) – A type of computer network that links computers inside a defined geographic region, such as a house, school, laboratory, university campus, or office building. Ethernet and wireless (known as wireless local area networks or WLAN) are the two most often used technologies for local area networks.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) – A computer network that links users to computer resources within the confines of a metropolitan area. Additionally, the phrase refers to the connectivity of multiple local area networks within a metropolitan region via point-to-point connections.
- Wide Area Network (WAN) – A large-scale telecommunications network designed primarily for computer networking. Leased telecommunications circuits are frequently used to create wide area networks. The internet may be thought of as a WAN.
What is the Purpose of a Local Area Network (LAN)?
Local Area Networks connect computers and enable shared access to printers, data, and other services. Peer-to-peer or client-server architectures are used to describe local area networks.
Related: What is a LAN? Understanding Local Area Networks
On a client-server local area network LAN, several client devices connect to a central server that manages application access, device access, file storage, and network traffic.
The Local Area Network server’s applications enable database access, document sharing, email, and printing. Without needing a central server, devices on a peer-to-peer local area network communicate data directly with a switch or router.
LANs can communicate through leased lines and services or over the internet via virtual private network technology. This network of linked LANs is referred to as a Wide Local Area Network (WLAN) or a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
WLANs transfer data through radio waves rather than cables and wires. Wi-Fi technology is a widely used standard in WLANs.
While a WLAN may look different, it functions the same way as a traditional LAN. WLANs are based on the IEEE 802.11 wireless data transmission standards.
As long as the devices implement WLAN technology, the Wi-Fi standards support the same interfaces as LANs, including printing and Internet access.
Applications of LANs
- In a network or group of computers, one computer is assigned the role of server, and it manages all the systems
- In the local area network, the software is stored on the server so that all the authorized users can use it
- LAN connects workstations in a building so that they can communicate with each other without the internet
- In this network, you can share resources like scanners and printers
- It’s a helpful network for software developers because they can share testing and development tools within the company
Local Area Networks (LANs): The Benefits for Businesses
Local Area Networks offer several advantages in business:
- Cost Savings – LANs enable considerable cost savings in Local Area Network hardware and resource pooling.
- Improved Storage Capacity – By consolidating all data into a single data storage server, the number of storage servers required is reduced while operational efficiency increases.
- Increased Flexibility – Data may be accessed from any device with an Internet connection, regardless of location.
- Efficient Communication – Files and communications may be exchanged in real-time and viewed from any device.
What is a Wide Area Network (WAN)?
A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that spans a broad geographic region. WANs may allow communication, information exchange, and much more between devices located worldwide through a WAN provider.
While WANs are critical for international commerce, they are also essential for everyday use. A WAN links several smaller networks, such as local area networks (LANs) and metro area networks (MANs). A WAN can be implemented via a public transmission system or a private network.
Often, these networks are built by service providers who subsequently lease them to companies, schools, governments, and the general public.
Regardless of their location, these clients can utilize the network to relay and store data or connect with other users, as long as they have access to the established WAN. Access can be given by various modes of communication, including virtual private networks (VPNs) or lines, wireless networks, cellular networks, or internet access.
WANs enable worldwide organizations to carry out their critical everyday activities without delay. Employees from any location can use a business’s WAN to exchange data, interact with coworkers, or stay connected to the organization’s larger data resource centre.
Applications of WANs
- A WAN is built to connect branch offices or remote employees working from home to the primary office. Students may rely on WANs to access library databases or conduct academic research in a university or campus context.
- Another company that makes use of a WAN is a bank, which has branch offices and ATM While the branches may be located throughout the United States or internationally, they are all connected via various secure links. Users include both bank staff and customers.
- The internet may be considered the world’s largest WAN since it is the world’s largest and most diversified kind of computer network.
Wide Area Networks (WANs): The Benefits for Businesses
As businesses expand and become more global, WANs enable them to communicate across branches, share information, and maintain connectivity.
When employees travel for business, WANs allow them to obtain the information necessary to perform their duties. Additionally, WANs enable companies to exchange information with customers and partners, such as B2B clients or customers.
WANs also provide a critical service to the public. Students may rely on WANs to access library databases or conduct university research. Consumers rely on WANs every day to communicate, finance, and shop.
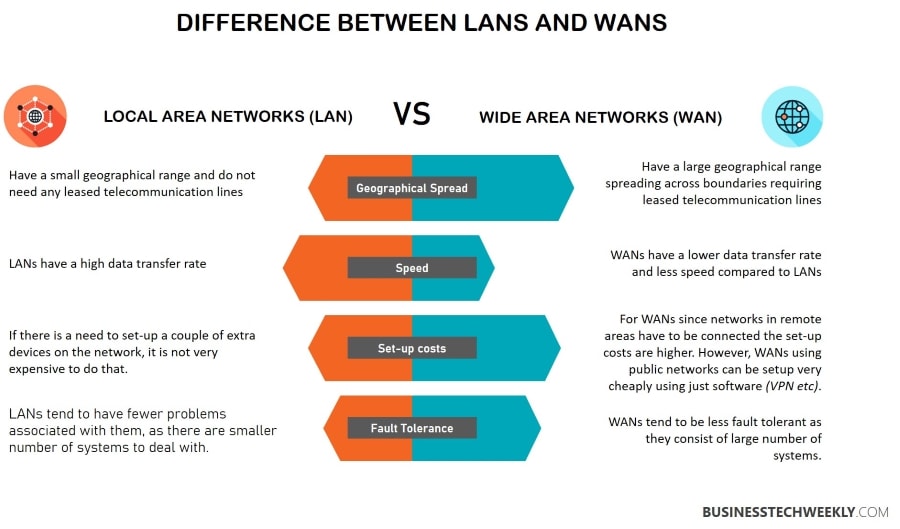
LAN vs WAN: The key differences
Local Area Network (LAN) |
Wide Area Network (WAN) |
|
Coverage |
Small geographical area limited to an office space or building |
Large geographical area, not limited to a country |
Ownership & Management |
A LAN is owned, operated, and managed by a customer |
WAN is owned, operated, and managed by several Service providers |
Security |
More secure |
Less secure |
Speed |
High – up to 1/10 Gbps |
Generally 100 Mbps |
Components |
Built using layer 1 and 2 devices such as switches and bridges. |
Built using layer 3 devices such as routers and multi-layer switches |
Technologies |
Ethernet, token ring |
MPLS, ATM, Frame Relay and ISDN |
Maintenance costs |
Less expensive to set up and maintain |
More expensive to set up and maintain |
Congestion |
Less congested |
More congested |
Physical Layer connectivity |
Copper and fiber medium |
Fiber medium |
Example |
Local office network |
The internet |
LAN vs WAN: Which Network works best for your business?
As mentioned previously, LANs and WANs are comparable in many respects, but they also have some critical distinctions. If your firm is contained within a single facility, a LAN is often all that is required.
However, if you have several sites scattered over multiple geographic regions or a large number of remote users, you’ll also need a WAN to keep everything, and everyone linked efficiently.
When building or updating your network, the most critical factor to consider is partnering with the right IT partner. This is especially critical if you are setting up or maintaining a wide area network (WAN).
Also Read: Finding a Technical Supplier for your Business
Collaborating with a partner who has expertise in managing many sites and interconnected networks will save you significant time and money.