Metropolitan Area Networks: A quick guide to MANs

A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a computer network in which two or more computers, communication devices, or networks that are physically separated but located in the same metropolitan metropolis are connected.
Metropolitan cities’ boundaries are defined by local municipal corporations. Hence, the bigger the Metropolitan city, the bigger the MAN, smaller a metro city smaller the MAN
Learn how MAN networks are constructed and used and the benefits they offer.
What is Metropolitan Area Network?
Many people get confused by the term Metropolitan Area Network. They think it’s only limited to urban areas, which isn’t the case. It’s a network that connects computers within a metropolitan area.
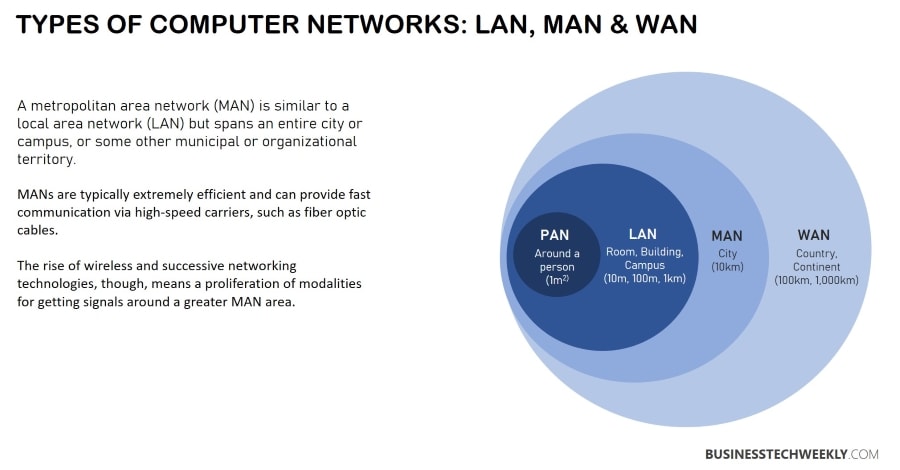
The area can be multiple cities, a single city, multiple towns, and an area with numerous buildings. As mentioned earlier, these networks are larger than Local Area Networks (LANs) and smaller than Wide Area Networks (WANs).
The term “Metropolitan” describes the size of the network instead of the demographics of the area. So, the difference must have been cleared now.
Characteristics of Metropolitan Area Networks: MAN vs WAN vs LAN
| Metropolitan Area Network
(MAN) |
Wide Area Network
(WAN) |
Local Area Network
(LAN) |
| Ownership of MAN can be public or private | A WAN may be owned by more than one organization | Ownership of LAN is private |
| MANs have an average transmission speed | WANs have low transmission speed | LANs have a high transmission speed |
| MAN propagation delays are moderate | WAN propagation delays are quite long | LAN propagation delays are short |
| MANs tend to be more congested | WANs are more congested than MANs | LANs tend to be less congested |
| The maintenance and design of MANs are more complex than LANs | The maintenance and design is of WANs is more complicated than LANs or MANs | LAN maintenance and design is straightforward |
| MAN has less fault tolerance | WAN has less fault tolerance | LAN has more fault tolerance |
How do Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) work?
Like other networks, it’s made of interconnected local area networks. In MAN, data doesn’t travel over a considerable distance; therefore, they’re more efficient than wide-area networks. A single organization doesn’t manage MANs. Instead, they combine networks of multiple organizations.
Metropolitan area networks use fiber optics for building connections between the local area networks. Organizations can get these fiber optic cables on lease from internet service providers. Sometimes the city government helps to build and maintain the fiber-optic network. Moreover, they lease the dark fiber to some private companies.
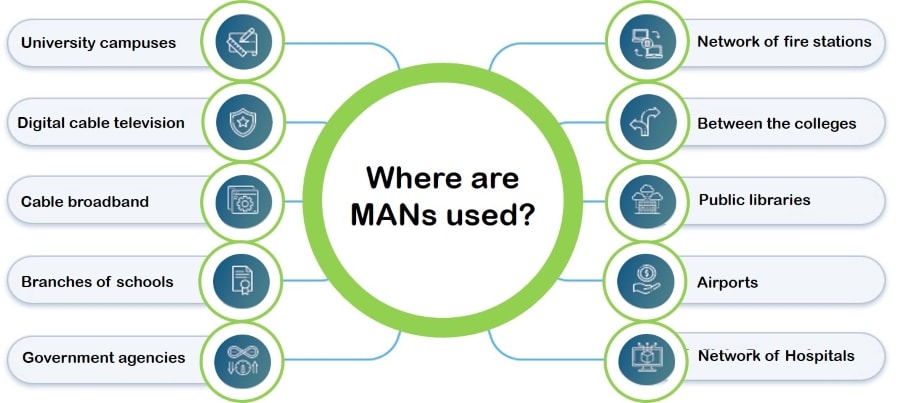
Uses of Metropolitan Area Networks
The main goal of MAN is to connect the dispersed LANs geographically. It helps to establish a communication link between LANs. A router facilitates the network connection by assisting the packets in identifying the path for information sharing. These networks are best operated between distances ranging from 5-50 km.
This data network is either used by a single organization in a group of buildings or by multiple interconnected organizations within the same city. You can’t consider it a WAN, but it’s larger than LAN. You can consider it a campus network if the interconnected buildings are on the same property.
It establishes the data connections between the buildings and the data center. Some link technologies like Dark fiber, WLAN, private 5G networks, and Ethernet runs are used for establishing connections.
- The primary aim of MAN is to connect computer networks across cities.
- Development and installation of a networking system that connects servers to communicate the network businesses and governments use to participate in activities such as chat, messenger, and video.
- There are many types of computer networks, but MAN is the most frequently utilized for intercity connectivity. Telecommunications operators must connect computer networks across kilometres to build a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
- The MAN Computer Network will improve communication efficiency, business efficiency, and network security.
- It is integrated with a cable television or radio network and offers both text and speech data transmission.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Examples
- A company may have a diverse portfolio of properties in separate districts within a city. To link these sites, the organization can link these buildings through an optical fibre to form a campus area network or MAN.
- A single city can be interconnected as a large single MAN to provide free Wi-Fi to all residents. It may also create separate MANs to link all traffic lights electronically and parking metres to create a metropolitan area network.
- A telecommunications company rents fibre connections in a city. Numerous businesses use them to connect, resulting in the formation of a massive MAN.
Advantages and Disadvantages of MANs
Like LAN and WAN, metropolitan area networks have some advantages and disadvantages. So, let’s discuss some of them.
Advantages
- Cheap and Easily Manageable – It’s cheap and easy to connect MAN with WAN. The data in MAN is centralized and easily manageable.
- High Speed – As fiber optics are used in this network, the data speed can easily reach 1000 Mbps. The transfer rate of files and database is quick.
- High Security – In terms of security, MAN is better than WAN.
- Internet Sharing – In MANs, users can share internet connections. It means multiple users can enjoy the same internet speed.
- Conversion Is Easy – When two or more LAN networks are combined, they form a MAN. So, the configuration and modification of LAN to MAN is easy.
Disadvantages
- Cybercrime Attacks – When we compare LAN and MAN, the MANs are more prone to cyber-attacks. It is due to the connectivity of a vast number of LANs. So if you want to avoid data leakage, you need to hire high-security staff.
- Difficult to Manage – When the number of LANs increases, it becomes difficult to manage. This issue arises mainly due to extra configuration and security problems.
- Speed Issue – Organizations that build the network on fiber optics don’t face speed issues. On the other hand, copper wires can significantly reduce the speed.
- High Fiber Optic Cost – MANs perform best on fiber optic, so to enjoy quick sharing and fast speed, you’ll have to bear the high upfront cost of fiber optic. Since it’s the combination of two or more LAN networks, you need more cables in the case of MAN.
- Not Easy to Set Up – For MAN set up, organizations need to call technical staff. The staff includes network troubleshooters and administrators.
Summary
A metropolitan area network (MAN) has historically referred to a private data network utilized by businesses in many buildings or by numerous geographically connected companies. It is more significant than a local area network (LAN) within a single building but not large enough to be termed a wide-area network (WAN).
As technology advances and more devices get linked, metropolitan area networks will continue to grow in popularity. Additionally, some use the term MAN to allude to the high-speed internet connectivity provided by 5G cellular technology across a city. In contrast, another possible future application for a MAN is a citywide network of autonomous cars exchanging position, traffic, and destination data.

