What Is Information Rights Management (IRM) and Why You Need It?

On this page:
What Is Information Rights Management?
It simply ensures that only authorized users can access or interact with certain information. This limitation provides a deeper level of protection in digital spaces.
By defining permissions, IRM can ensure that only those with permission have access to email messages and other digital communications.
For example, you could protect an email containing new, confidential business strategies with IRM. This way, only specific recipients will be able to view or resend the email.
This control is also an important element in enforcing corporate policies on how and when confidential information should be handled and distributed.
1. Definition of Information Rights Management
Information rights management (IRM) is a more refined and narrower subset of digital rights management that focuses on securing sensitive data. IRM is specifically tailored for intellectual property and confidential documents.
This is what distinguishes it from wider digital rights management, which usually focuses on media copyright.
By including a wide range of applications—from email clients to document management systems—IRM goes beyond classifying content and controlling access rights.
Industries such as healthcare and finance are dependent on this integration. Their clients’ and their proprietary information is always their highest priority.
The IRM market is estimated to be worth $2.34 billion in 2024, and is expected to grow to $5.43 billion by 2029.
2. Purpose and Goals of IRM
The main objective of IRM is to prevent sensitive information from being handled inappropriately. It is crucial to helping organizations stay compliant with data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
These regulations demand high levels of oversight for personal and sensitive information.
IRM provides organizations the ability to address these demands by controlling who has the right to view or edit that information. IRM is especially important for managing the spread of sensitive proprietary information.
For example, a tech company can use IRM to ensure that its trade secrets remain within the organization, thus preventing potential leaks.
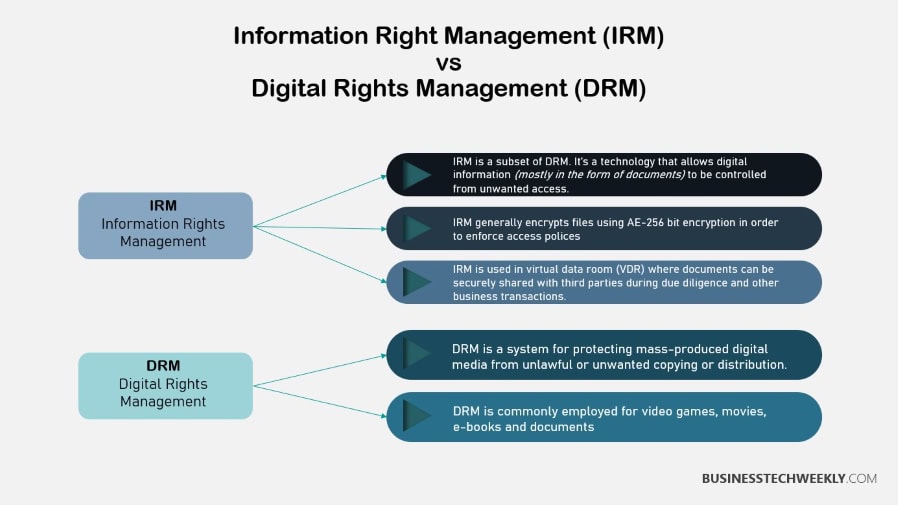
3. Difference Between DRM and IRM
Though both digital rights management (DRM) and IRM are used to secure data, their purposes are distinct. DRM is widely used today on media and entertainment content, controlling rights to films, songs, and other digital media.
By comparison, IRM is much more aligned with document security and shielding the enterprise’s confidential information.
IRM provides enhanced capabilities such as automating watermarking documents, expiring access to documents, and revoking access as well as tracking the use of the documents. Each of these features are aimed at fulfilling enterprise organization requirements for protecting data.
They help you make sure only the right people can view sensitive information.
Importance of Information Rights Management
Protecting Sensitive Data
Information Rights Management (IRM) is instrumental in protecting sensitive information from data breaches and information leaks, functioning as an effective document rights management solution.
It stops unauthorized users from viewing sensitive documents, ensuring that only authorized users have access permissions. Think of it as having a strong deadbolt on a door that prevents unwanted access to confidential data.
IRM employs encryption and specific IRM policies to obfuscate data, rendering it useless to anyone who lacks the suitable data key.
This additional security provides another level of protection against future threats.
By implementing IRM features, organizations can greatly reduce the chances of a data breach, keeping information safe and minimizing the risk of financial loss due to unauthorized copying or access management issues.
Ensuring Compliance with Laws
IRM enables organizations to comply with various data protection regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. IRM gives you audit trails that show every action performed on a document.
This also creates an easy way to prove compliance at audit time.
The importance of IRM spans the lifecycle of information content, offering a comprehensive structure that incorporates rights management technology to meet security standards and compliance regulations.
By leveraging the capabilities of Azure Rights Management Service, your organization can remain compliant and avoid legal issues, while also enhancing document rights management practices.
Overall, IRM gives organizations the confidence to demonstrate compliance with operational and regulatory requirements, ensuring that sensitive information is protected against unauthorized use and access management issues.
Maintaining Document Control
By allowing organizations to limit who can share or view sensitive documents, IRM plays an important role in keeping data secure. Set permissions to prevent others from copying, printing or sharing your documents.
This helps ensure that sensitive information is protected and only shared with the appropriate parties.
This degree of control is important because it has a direct effect on data security as a whole.
When you have solid document control in place, your data doesn’t stray beyond your organization’s borders. This simple practice greatly reduces the chances of unintentional and even malicious leaks.
IRM protects your sensitive information from unauthorized access by adding a seal of protection that moves with your document. So no matter where your document travels, it’s secure!
This detailed framework is critical for any organization that seeks to have a data protection program.
Key Features of IRM Systems
Access Control Mechanisms
Access control features in IRM systems act as a gatekeeper to sensitive data. You have varied mechanisms at your disposal, each providing a distinct level of granularity so that you can control who sees what and when.
Role-based access assigns permissions based on a user’s role within your organization.
On the other hand, attribute-based access grants or denies access according to specific attributes, like a user’s location or the type of device being used. Permission levels are really, really important here.
They decide if users can only view, edit or print documents, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
With granular permissions, you can set detailed access rules, allowing you to further refine who can do what to each document. For example, a project manager may have the ability to edit a document, while a team member is limited to simply viewing that document.
This level of granular control ensures that your data is protected and accessible only to the individuals you want to have access.
RELATED: What RBAC? UnderstandingRole-based Access Control
Encryption and Security Protocols
Encryption ensures that any sensitive documents you save in your IRM system are transformed into unreadable codes, which can only be decoded by authorized users.
Common methods used such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) provide maximal security to your data.
Security protocols, such as SSL/TLS, complement encryption by ensuring both data integrity and confidentiality while data is in transit. They help to make sure your documents stay locked, safe and secure even when shared or accessed remotely.
Encryption protects not just the sharing of documents, but strengthens the very core of your security infrastructure.
When you send a file, encryption ensures it reaches the intended person without any unauthorized peeking, providing peace of mind in a digital world.
Persistent Protection Across Platforms
With IRM, even if someone copies them elsewhere or prints them out, the documents are still protected. Whether on a desktop in the office or a smartphone on the go, security remains an important factor.
This continuous defense is critical, particularly in today’s hybrid workforce environment where access occurs from multiple devices and places.
It helps achieve security for your data, no matter where it’s accessed—be it a cloud environment or on-premises infrastructure.
Whether you’re on PC, Mobile, or Console, repeatable security processes have you covered. You can move between devices without fear of being exposed to a vulnerability.
This consistent, uniform protection framework promotes continued trust in your document security, no matter where or how you operate today.
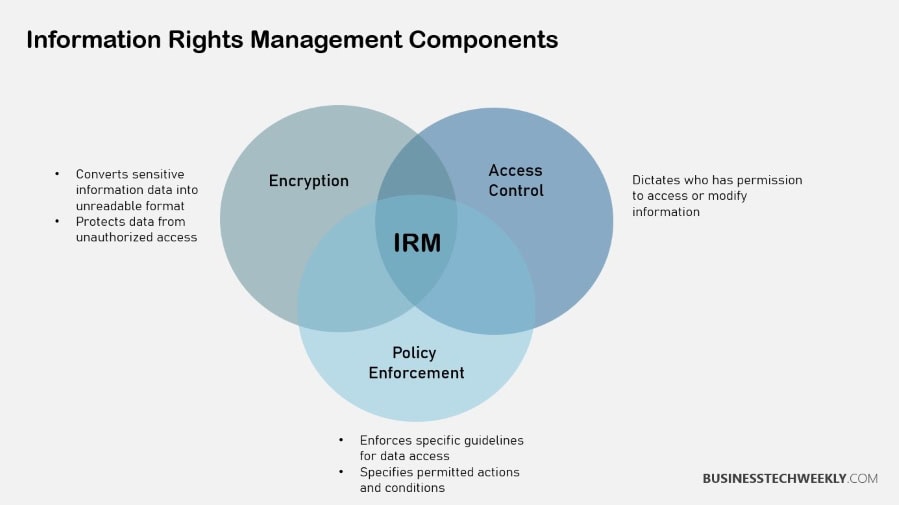
Components of an IRM Strategy
To develop an effective IRM strategy that works for your organization, consider essential components such as rights management technology and specific IRM policies.
These components must interoperate in unison to protect your organization’s data while ensuring that authorized users can quickly access sensitive information with appropriate permissions management.
Policy Development and Enforcement
Developing strong IRM policies begins with understanding the unique needs and objectives of your organization. You need to establish specific protocols for document storage, access, and data distribution.
These policies should also be in accordance with your wider organizational objectives, making sure that data protection efforts don’t obstruct the flow of work.
Once these imperatives are in place, rigorous enforcement of these policies is essential to ensure compliance and accountability. Ongoing evaluation and adjustment of your policies and procedures should be a continuous practice.
This ensures your IRM approaches stay relevant and effective as technologies and threats continue to change.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating IRM with your existing IT framework can help improve document security by offering uniform protection no matter where files are stored or shared. This seamless integration allows for data to be protected without causing disruption to workflows.
However, these efforts may run into obstacles when addressing legacy systems that cannot accommodate today’s IRM solutions.
Tackling these challenges takes foresight and, at times, innovative thinking to make sure that all systems work together and are protected.
User Training and Awareness
Educating users about IRM policies and procedures is essential to successful adoption. When users understand the importance of security measures, they’ll be more compliant, and your risk of a data breach decreases significantly.
Fostering a culture of understanding around the need to protect data can be done through accessible communication campaigns and ongoing education in the form of annual trainings.
Ongoing education is key to creating a security-first mindset throughout an organization, empowering every individual to help protect their organization’s information.
Advantages of Adopting IRM
Enhanced Data Security
There are many key advantages that come along with implementing Information Rights Management (IRM) solutions that organizations should consider. One of the most important is improved data security.
IRM serves as a powerful, extra-level shield against data breaches, leaks and loss by utilizing sophisticated access controls and encryption. These capabilities prevent unauthorized users from seeing or interacting with sensitive data.
For example, a financial institution can leverage IRM by encrypting sensitive client data. This preemptive process limits access to the information only to those employees whose role requires it.
This process helps not just to secure sensitive data, but to stop inappropriate sharing before it happens.
Proactive measures, such as real-time monitoring and alerts, protect your sensitive information even before a breach has a chance to happen.
Improved Regulatory Compliance
Further, IRM is a key factor in enabling organizations to comply with regulatory requirements. With firm control over who can access and manipulate data, organizations can better comply with data protection laws such as GDPR or HIPAA.
RELATED: Understanding Data Governance Policies: Best Practices for Secure Data Management
This congressional oversight is crucial to protecting sensitive information. This helps them avoid potentially hefty fines, but also helps them earn trust with their clients and stakeholders.
For auditors, IRM makes the audit process much easier by providing documented evidence of how data is handled.
During an audit, a highly mature organization can quickly demonstrate compliance.
They achieve this by proving how they manage and track third-party data access, which simplifies their internal audit processes while also expediting external audits.
Flexibility and Scalability
The flexibility and scalability of IRM systems are invaluable in today’s evolving regulatory climate. With IRM solutions, you’ll find they are not just one-size-fits-all solutions.
As data protection requirements continue to increase, IRM systems are easily scalable, providing complete coverage without frequent and costly system overhauls.
For instance, when regulatory requirements change, IRM policies can be modified to comply with new regulations while minimizing operational impact.
This versatility is key for maintaining a leading position in an environment of ever-changing data security demands.
Challenges in Implementing IRM Solutions
Implementing Information Rights Management (IRM) solutions is not as simple as it sounds. Organizations face no shortage of challenges, but each deserves thoughtful consideration. IRM is an art form, requiring careful consideration and expert implementation.
The truth is, rolling out IRM is not always straightforward, so understanding when and how to use it is key.
Downsides of IRM-protected sites include the fact that they don’t allow for double-encryption of files, which poses difficulties in certain circumstances.
Complexity of Integration
Beyond the change management aspect, integrating IRM with existing workflows is a technical challenge.
Systems don’t always play nicely with one another, often creating not just incompatibility, but chaos.
For example, replication in Office 365 goes about as fast as molasses in winter, making IRM use even more difficult.
As an example, within the Life Sciences industry, which heavily utilizes digitally-signed documents, IRM can be very difficult to implement. To get past these challenges, careful planning and execution will be key.
An underlying zero-trust security paradigm is required, but difficult to uphold.
User Adoption and Resistance
User resistance is a major barrier when implementing any new IRM technology. For those users who come from a legal background, the transition to IRM practices can be especially difficult.
However, they require seamless access to sensitive information, complicating this transition immensely.
To encourage user buy-in, organizations must use strategies to promote IRM, including providing robust training and effectively communicating IRM’s benefits.
Addressing these concerns and ensuring strong support during the transition will go a long way toward making the shift a little more smooth.
Cost and Resource Allocation
Financial considerations are another major factor when evaluating rights management technology for implementing IRM solutions.
Providing adequate resources for these initiatives helps ensure they are set up to succeed, while assessing the return on investment is crucial in justifying the time and money spent on document rights management.
Use Cases for Information Rights Management
Corporate Data Protection
IRM is critical to protecting corporate data assets from loss and theft. Whether you’re in HR, finance, or a public-facing department with sensitive company data, protecting it should always come first.
IRM helps to ensure that your data is always safe from those who should not have access to it and avoid a data breach.
However, companies are put at great risk when data security is breached. Breaches result in direct financial loss, legal action and loss of reputation.
IRM is useful when attempting to avoid these risks by implementing robust access controls and monitoring data usage.
Powerful Information Rights Management (IRM) tools are essential for protecting the most sensitive information. They help ensure that only people with the right permission level are able to view or edit sensitive information.
Secure Document Sharing
In dynamic, collaborative environments, sharing documents securely is more important than ever. With IRM, you can confidently share files, sure that only the people you want to have access are the people who do.
This system, powered by IRM, employs access controls that stop anyone from sharing or distributing confidential documents.
Or share the latest financial report to your entire team. With IRM, you can ensure that only the people on your team who need to see it can access it.
Keeping documents confidential while collaborating is crucial to keeping business secrets safe, winning contracts, and adhering to business regulations.
With IRM you can make better decisions through collaboration, while controlling access to your most sensitive data.
Intellectual Property Safeguarding
Protecting IP rights is another key use case for IRM. If your organization produces proprietary content, IRM protects it from being copied and circulated without your permission.
Imagine a technology start-up that has developed a new, innovative software algorithm. IRM makes it possible to allow only licensed users to access the code, preventing it from being stolen or misused.
That protection fosters innovation and creativity by allowing creators to maintain control over their valuable assets.
Once your IP is protected, you won’t have to worry about bad actors stealing or misusing your hard work while you’re busy creating your next big innovation.
Key Takeaways
Information Rights Management (IRM) is your next line of defense to protect your data.
It provides creative strategies and tools for determining how to protect sensitive information and manage access to it.
With IRM, you protect your sensitive content from being accessed by unauthorized users and help maintain compliance with data regulations.
- Information Rights Management (IRM) is key to protecting access to sensitive information. It provides an assurance that only authorized users can access or change that information.
- Adopting IRM also empowers organizations to adhere to data protection laws such as GDPR and HIPAA. This proactive approach substantially reduces the chance of incurring legal penalties.
- IRM systems improve document security by applying encryption and access controls. This additional step goes a long way in making it more difficult for unapproved users to obtain access.
- Making IRM fit with your existing IT environment can be challenging. It’s actually very important for integrating and protecting corporate data seamlessly, everywhere.
- Effective user training and awareness greatly contribute to the success of IRM policies. In addition, they do a lot to promote a healthy culture of security throughout the organization.
- Despite the obstacles to implementation, IRM offers substantial benefits by better protecting our nation’s intellectual property and improving the security of federal data.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Information Rights Management important?
Information rights management (IRM) is imperative for protecting intellectual property, proprietary research, and sensitive data.
By implementing Azure Rights Management Service and specific IRM policies, it safeguards against cyber attacks and information leaks, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
What are the key features of IRM systems?
IRM systems, utilizing rights management technology, provide encryption, user authentication, and access by permission levels.
They enable robust audit trails for tracking document usage and access, while allowing for dynamic revocation of permissions, ensuring document rights management long after distribution.
What components make up an IRM strategy?
A comprehensive IRM strategy should feature policy development, end-user education, and technology adoption through rights management technology, ensuring compliance oversight.
It’s crucial to know what sensitive data you have and determine specific IRM policies for access management.
What are the advantages of adopting IRM?
IRM helps protect sensitive data and ensure organizational compliance through rights management technology.
This approach avoids the pitfalls of data breaches, unauthorized data sharing, and enhances document rights management to maintain customer trust.
What challenges can occur when implementing IRM solutions?
It takes more than just technology—it requires seamless integration with existing systems, user training, and ongoing management of rights management technology.
User compliance and adapting to changing threats are major challenges as well.
What are some use cases for Information Rights Management?
IRM is already in widespread use in other critical industries such as finance, healthcare, and legal services.
It shields sensitive documents like contracts, financial statements, and patient records. It provides tight data security whether you’re working internally or with external collaborators.

